Le Campylobacter Vanessa Roch Es Technicienne en

Links between the ASCUS and the HPV in the 20-30 year-old women and 40-50 year
Vanessa Roch
LaboratoryADMED Pathology
Neuchâtel, Switzerland
Mentor: Patricia Besson Vuithier
Introduction
ASCUS (Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance) is part of Bethesda 2001
system. These are squamous cells, in the cervix, with an enlarged nucleus, slightly irregular
with sometimes a discret peri nuclear halo. (As you can see on the left hand of this picture).
Its origin, as its name indicates, is not determined. It can result as well from a simple
inflammatory reaction, like a sign of CIN (Cervix Intraepithelial Neoplasia) or more rarely a
carcinoma and be associated with a HPV infection. HPV (human papillomavirus) is a
sexually transmitted virus and is the main cause of cervix cancer.
Aim
My work consists in comparing the category ASCUS in
search of HPV into two categories of women, the 20-30
year-old women and the 40-50 year-old women in order
to see with which degree the ASCUS and the HPV are
connected. The study was made over the year 2010-
2011. The purpose of my work is also to demonstrate
that this category has its importance in the Bethesda
system.
Material and Methods
Classification of the results of HPV on the samples
ASCUS of 185 women between 20-30 years and 199
women between 40-50 years of 2010-2011. The HPV
results were classified by category of age as well as if they
are positive or negative. Classification of the positive HPV
in high HPV risks (HR), low risk (LR) or multiple infection
high risk and low risk (HR/LR) was carried out. Search for
biopsy associated with ASCUS.
Results and interpretations
Discussion and Conclusion
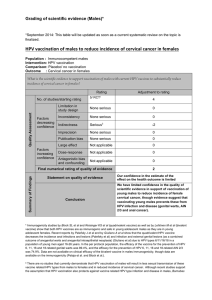
For the 20-30 year-old women, the diagnosis of ASCUS is important because it allows not to miss many high risk HPV.
Indeed, in classifying these women as being negative, 82 women at risk of developing a cancer would have had no adequate
follow-up.(That’s mean 50%).
On the other hand, for the 40-50-year-old women, a diagnosis of ASCUS is very often associated with negative HPV. 75%of
these women are thus followed and present no risk of developing a cancer.
59%
16%
25%
HPV HR HPR LR HPR HR/LR
55%
17%
28%
HPV HR HPV LR HPV HR/LR
53%
47%
Women between 20-30 years
2010-2011
HPV +
HPV -
24%
76%
Women between 40-50 years
2010-2011
HPV +
HPV -
1
/
1
100%