SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE

SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE
DÉPARTEMENT DE
2015-2016

DÉPARTEMENT DE SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE 2015-2016
1
Le département d’économie de
Glendon vise l’excellence dans
l’enseignement et la recherche.
Il est intégré à un petit campus
bilingue qui valorise la diversité
et l’engagement
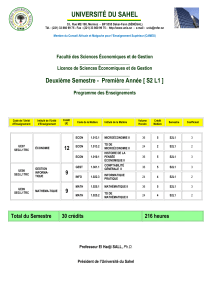
communautaire.
DÉPARTEMENT DE SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE
Bureau : 327 Pavillon York
Directeur : Vincent Hildebrand
Secrétaire administrative : Aurore Coco
Téléphone : 416.487.6712
Télécopieur : 416.487.6852
Courriel : [email protected]
DÉPARTEMENT DE SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE 2015-2016
2
TABLE DES MATIÈRES
01 NOUS CONTACTER
03 AU SUJET DE NOTRE PROGRAMME
05 NOTRE CORPS ENSEIGNANT
07 QU’EST-CE QUE L’ÉCONOMIE?
07 QUE PEUT-ON FAIRE AVEC UNE FORMATION EN SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE?
09 QUESTIONS FRÉQUEMENT POSÉES
11 CLUBS D’ÉCONOMIE
11 BOURSES D’ÉTUDES DU DÉPARTEMENT
12 ORIENTATION PÉDAGOGIQUE ET RESSOURCES
POUR LES DESCRIPTIONS DE COURS, VOIR L’ENCART

DÉPARTEMENT DE SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE 2015-2016
3
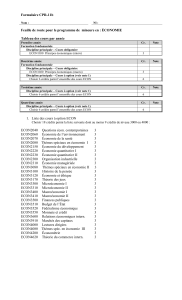
AU SUJET DE NOTRE PROGRAMME
NOTRE MISSION
Le département d’économie de Glendon vise l’excellence dans l’enseignement et la
recherche. Il est intégré à un petit campus bilingue qui valorise la diversité et
l’engagement communautaire. Nous offrons des programmes interdisciplinaires qui
permettent de combiner une formation en économie avec des champs d’études
connexes tels que les mathématiques, les sciences politiques, les études
internationales, etc.
NOS PROGRAMMES
Notre département offre un programme en science économique qui s’adresse
aux besoins de deux catégories d’étudiants. Le programme offre aux étudiants qui
se dirigent vers une carrière d’économiste, des cours de formation de base et des
cours d’économie théorique et appliquée. Ces cours permettent l’acquisition d’une
base solide et contemporaine préparant l’étudiant à des études au niveau de la
maîtrise en économie ou en science commerciale.
Le programme d’économie est aussi destiné aux étudiants qui ne veulent pas
nécessairement devenir des économistes, mais qui désirent plutôt connaître les
fondements de la science économique pour le défi intellectuel qu’elle représente, la
place qu’elle tient dans le monde d’aujourd’hui, et pour le rôle qu’elle occupe dans
des domaines comme les secteurs juridiques, politiques et diplomatiques, les
affaires, la fonction publique et l’administration.
De plus, le département offre un programme en économie et commerce. Ce
programme spécialisé a pour but de permettre aux étudiants qui désirent faire
carrière dans le monde des affaires de suivre des cours à vocation commerciale.
Nos programmes préparent nos étudiants pour des études graduées en économie
ou commerce, ou pour une carrière en enseignement et recherche, dans le monde
des affaires comme les secteurs financiers et bancaires, et dans les milieux
politiques et administratifs. Plusieurs de nos diplômés ont de brillantes carrières
dans ces domaines ou poursuivent leurs études graduées dans des universités
prestigieuses.
NB : Les règlements en vigueur au moment de votre inscription dans
le programme sont ceux qui régissent votre diplôme. Prière d'en
prendre connaissance, en consultant l'annuaire de premier cycle de
l'Université York de cette année-là.
DÉPARTEMENT DE SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE 2015-2016
4

DÉPARTEMENT DE SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE 2015-2016
5
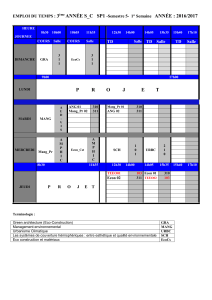
NOTRE CORPS ENSEIGNANT
CAN ERUTKU
BA.A (HEC Montreal), MSc (HEC Montreal), PhD (Université Laval)
Professeur agrégé, 364 Pavillon York
Téléphone: 416.736.2100 poste 88127
Courriel : cerutku@glendon.yorku.ca
http://glendon.yorku.ca/canerutku
Enseignement et domaines de recherche : Organisation industrielle, économie des
ressources naturelles et de l’environnement, microéconomie appliquée, antitrust.
OMAR F. HAMOUDA
BA (ESSEX), MA (McMaster), PhD (McGill)
Professeur agrégé, 365 Pavillon York
Téléphone: 416.487.6778
Courriel : [email protected]
http://www.glendon.yorku.ca/jid
Enseignement et domaines de recherche : Économie du développement; politiques
économiques internationales et questions monétaires.
VINCENT HILDEBRAND
BA (Paris IX-Dauphine), MA, PhD (York)
Professeur agrégé, 363 Pavillon York
Téléphone: 416.736.2100 poste 88591
Courriel : [email protected]
http://dept.econ.yorku.ca/~vincent
Enseignement et domaines de recherche : Économie du travail, micro-économétrie,
finances publiques, immigration.
MARIE LAVOIE
BA, MA, (Laval) MSc, PhD (Sussex)
Professeur agrégé, 210 Manoir Glendon
Téléphone: 416.736.2100 poste 88149
Courriel : [email protected]
Enseignement et domaines de recherche : Économie de la science et de la
technologie, gestion de l’innovation, capital humain et capital social, économie
industrielle, microéconomie, macroéconomie, l’éducation dans le domaine des
sciences et du génie.
DÉPARTEMENT DE SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE 2015-2016
6
NICOLAS-GUILLAUME MARINEAU
BA (York), MA, Ph.D. (Queen’s University)
Professeur adjoint, 329 Pavillon York
Téléphone: 416.736.2100 poste 88124
Courriel: martinea[email protected]
Enseignement et domaines de recherche : Économie publique, économie politique,
théorie microéconomique.
XAVIER DE VANSSAY
BA, Agreg. Com. (Brussels); DEA, DESS (Paris); MA, PhD.(Simon Fraser)
Professeur titulaire, 339 Pavillon York
Téléphone: 416.736.2100 poste 88153
Courriel : [email protected]
http://www.glendon.yorku.ca/devanssay
Enseignement et domaines de recherche : Économie internationale, finances
publiques, finance.

DÉPARTEMENT DE SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE 2015-2016
7
QU’EST-CE QUE L’ÉCONOMIE?
Fondamentalement, l’économie s’intéresse à la production, distribution et
consommation de biens et services: comment les décisions relatives à la production
sont-elles prises, comment les biens et services sont-ils produits, et qui consomme
quoi?
L’économie se divise en deux branches interdépendantes. La microéconomie étudie
le comportement individuel des agents économiques et son impact sur la
détermination des prix dans des marchés spécifiques ainsi que sur l’allocation des
biens et services par des entreprises qui se font concurrencent. La macroéconomie
étudie l’économie dans son ensemble et examine les facteurs qui déterminent la
production nationale, l’emploi et le niveau des prix dans un pays.
L’économie est une science sociale reliée à des disciplines comme la sociologie et les
sciences politiques. La différence entre l’économie et les autres sciences sociales est
son emphase sur des aspects du comportement humain qui sont quantifiables. Pour
cette raison, l’économie repose généralement plus sur la formalisation
mathématique et l’analyse de données que les autres sciences sociales.
QUE PEUT-ON FAIRE AVEC UNE
FORMATION EN SCIENCE
ÉCONOMIQUE?
Une formation en économie offre une excellente préparation pour une carrière dans
les secteurs financiers et bancaires, dans les domaines de la fiscalité et des échanges
commerciaux, dans la politique et la fonction publique, ou comme planificateur
stratégique et consultant. Par ailleurs, elle ouvre la porte à des études graduées qui
elles mêmes amènent à l’enseignement et la recherche.
DÉPARTEMENT DE SCIENCE ÉCONOMIQUE 2015-2016
8
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
1
/
15
100%