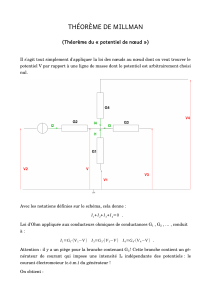
cours - Alain Camanes

Définition 1 (Relation binaire)
E G ⊂E×ER= (E, G)E
Notation.
(x, y)∈E×E(x, y)∈G x y xRy
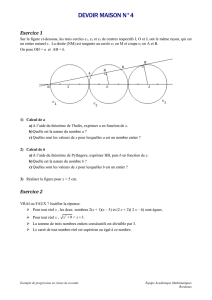
Exercice 1.
Définition 2 (Réflexivité, (Anti)symétrie, Transitivité)
RER
(i)x∈E xRx
(ii)x, y ∈E xRy yRx
(iii)x, y ∈E xRy yRx x =y
(iv)x, y, z ∈E[xRy yRz]xRz
Exercice 2.
Définition 3 (Relation d’équivalence)
RE E
Exercice 3.
Définition 4 (Classe d’équivalence)
RE x ∈E
x x cl(x){y∈E;xRy}
Exercice 4. x y xRy xey=yexR
x
x
Proposition 1 (Partition)
RE
RE
Définition 5 (Congruences)
(z, p)∈R×Z
(i)x y z x ≡y[z]k
x=y+kz
(ii)m n p n ≡m[p]k
n=m+kp

Propriété 2 (Congruence & Opérations)
a, a0, b, b0∈Zm, n ∈N?
(i)a≡b[n]a0≡b0[n]a+a0≡b+b0[n]
(ii)a≡b[n]a0≡b0[n]aa0≡bb0[n]
(iii)a≡b[n]m∈Zam ≡bm [nm]
Définition 6 (Relation d’ordre)
RE E
Exercice 5.
Notation.
4E A ⊂E x ∈E
Définition 7 (Ordre total / partiel)
(x, y)∈E2x4y y 4x4
4
Exercice 6.
Définition 8 (Majorant, Minorant)
(i)x A ∀a∈A, a 4x A
(ii)x A ∀a∈A, x 4a A
(iii)A A
Exercice 7.
1. (R,6)A1=] − ∞,3]
2. (R,6)A2=] −1,1]
3. (R,6)A3=1
n, n ∈N?
Définition 9 (Plus grand / petit élément)
(i)x A ∀a∈A, a 4x x ∈A
(ii)x A ∀a∈A, x 4a x ∈A
Exercice 8.
Théorème 1 (Maximum, Minimum)
(i)A A max(A)
(ii)A A min(A)
Définition 10 (Borne supérieure / inférieure)
(i)x A
Asup(A)
(ii)x A
Ainf(A)

Exercice 9.
1.
2. A B A ⊂B
sup Asup B
Théorème 2 (Comparaison max / sup)
(i)A A
sup(A) = max(A)
(ii)A A
inf(A) = min(A)
Exercice 10.
Définition 11 (Axiomatique de Peano, H.P.)
(0,N, s)N0Ns
N N
(i)Application successeur. s
(ii)s(N) = N\{0}
(iii)Axiome de récurrence. A⊂N0∈A A s A =N
Notations.
n s(n) = n+ 1
n+0 = n n+s(m) = s(n+m)
n n −1
Propriété 3 (Relation d’ordre sur N)
(m, n)∈N2k m =n+k m n
n6m6N
Théorème 3 (Récurrence faible)
n0P
n0
(i)P(n0)
(ii)∀n>n0P(n)P(n+ 1)
n>n0P(n)
Théorème 4 (Récurrence forte)
n0Pn0
(i)P(n0)
(ii)∀n>n0∀k∈Jn0, nK,P(k)P(n+ 1)
n>n0P(n)
Exercice 11. (un)u0= 2, u1= 3 n∈Nun+2 = 3un+1 −2un
n∈Nun= 2n+ 1

Théorème 5 (Théorème de l’élément minimal)
N
Exercice 12.
Théorème 6 N
R(R,+,·)
6
Notations.
(x, y)∈R2
x < y x 6y x 6=y
x>y y 6x
x > y y 6x x 6=y
Propriété 4 (Relation d’ordre & Opérations (admis))
(x, y, z)∈R3
(i)x6y x +z6y+z
(ii)x>0y>0xy >0
Exercice 13. x, y, z ∈Rz>0x>y xz >yz
Théorème 7 (Caractérisation des bornes sup / inf)
ARm∈R
(i)A m = inf(A)
∗ ∀ x∈A x >m
∗ ∀ ε > 0,∃x∈A;m6x<m+ε
(ii)A M = sup(A)
∗ ∀ x∈A x 6M
∗ ∀ ε > 0,∃x∈A;M−ε<x6M
Exercice 14. A=n(−1)n+1
n+1 , n ∈No
Théorème 8 (Théorème de la borne supérieure (admis))
R
Théorème 9 (Théorème de la borne inférieure)
R
Propriété 5 (Caractérisation des intervalles de R)
IR∀(a, b)∈I2a6b[a, b]⊂I
Définition 12 (Droite numérique achevée)
R R =R∪ {−∞,+∞}
6R∀x∈R, x 6+∞ −∞ 6x

R
+−∞ y∈R+∞
−∞ −∞ −∞ n.d.
x∈R−∞ x+y+∞
+∞n.d. +∞+∞
× −∞ y∈R?
−0y∈R?
++∞
−∞ +∞+∞n.d. −∞ −∞
x∈R?
−+∞xy 0xy −∞
0n.d. 000n.d.
x∈R?
+−∞ xy 0xy +∞
+∞ −∞ −∞ n.d. +∞+∞
Définition 13 (Voisinage)
a∈RW a
(i)a∈RW a
(ii)a= +∞c W =]c, +∞[
(iii)a=−∞ c W =] − ∞, c[
Exercice 15. a∈RV(a)aV(a)
N,Q,D
Théorème 10 (Rest archimédien)
Rx∈R?
+y∈Rn∈Nnx >y
Exercice 16. x∈Rn n 6x<n+ 1
Définition 14 (Partie entière)
x∈Rn n 6x<n+ 1 xbxc
Théorème 11 (Densité)
(i)Q R (x, y)∈R2x<y ]x, y[∩Q6=∅
(ii)R\Q R (x, y)∈R2x<y ]x, y[∩(R\Q)6=∅
Définition 15 (Nombre décimal)
x∈Rx n 10nx∈Z
D
Exercice 17. R
Définition 16 (Valeur décimale approchée)
x n a a ·10−n
x10−n|x−a·10−n|<10−n
a·10−n6x
Exercice 18. x∈Rx
1
/
5
100%