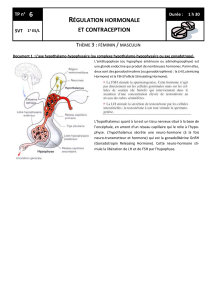
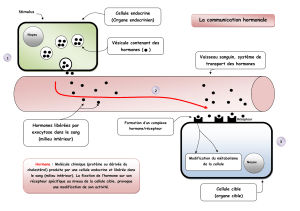
LE COMPLEXE HYPOTHALAMO

Physiologie Endocrine
Appareil Hypothalamo-Hypophysaire
1
LE COMPLEXE HYPOTHALAMO-HYPOPHYSAIRE
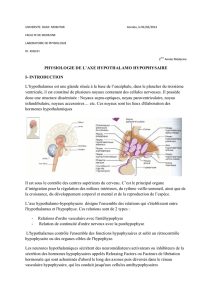
I - HYPOTHALAMUS ET HYPOPHYSE POSTERIEURE
A - Rappel anatomo-fonctionnel
B - Les neuro-hormones hypothalamiques
C - L’ocytocine
D - L’hormone antidiurétique (ADH)
II - HYPOPHYSE ANTERIEURE
A - Anatomie et histologie fonctionnelles
B - Nomenclature
C - Contrôle des sécrétions de l’anté-hypophyse
D - Hormone Thyréothrope
E - Hormones Gonadotropes
F - Pro-opio-mélanocortine (POMC)
G - Axe somatotrope
H - Prolactine
HYPOTHALAMUS et HYPOPHYSE POSTERIEUREHYPOTHALAMUS et HYPOPHYSE POSTERIEURE
A – RAPPEL ANATOMO-FONCTIONNEL
B – NEUROHORMONES HYPOTHALAMIQUES
C – L’OCYTOCINE
D – L’HORMONE ANTI-DIURÉTIQUE

Physiologie Endocrine
Appareil Hypothalamo-Hypophysaire
2
RAPPEL ANATOMIQUE
RAPPEL ANATOMIQUE
Noyaux hypothalamique sécréteurs de
Libérines et inhibines
Chiasma optique
Lobe antérieur Lobe postérieur
Corps mamillaire
Hormones anté-hypophysaires
Aff. corticales
Aff. Tronc Cérébral
Art. hypophysaire
supérieure
Veine durale
Plexus primaire
Plexus secondaire du
système porte
hypophysaire
Eminence
médiane Tige
pituitaire
Hypophyse
postérieure
RAPPEL D
RAPPEL D’
’ANATOMIE VASCULAIRE
ANATOMIE VASCULAIRE

Physiologie Endocrine
Appareil Hypothalamo-Hypophysaire
3
FONCTIONS ET S
FONCTIONS ET SÉ
ÉCR
CRÉ
ÉTIONS DES NOYAUX
TIONS DES NOYAUX
HYPOTHALAMIQUES
HYPOTHALAMIQUES
Noyaux Sécrétions
neuro-hormonales Principales fonctions
correspondantes
Supraoptique
• H. antidiurétique (ADH) +++
• Ocytocine +
⇒ Osmorégulation
⇒ Contraction utérine et éjection du lait
Paraventriculaire
- N. magnocellulaires
- N. parvocellulaires
• ADH + et Ocytocine ++
• TRH, CRH
• VIP (vasoactive intestinal pept.)
⇒ Idem supra
⇒ Régul. fonctions thyroïdienne et corticotrope
⇒ Sécrétion de Prolactine ( ?)
Suprachiasmatique ---------- ⇒ Rythme circadien (fonction « pace maker »)
Arqué • GHRH
• GnRH
• Dopamine
• Somatostatine (SS ou SRIF)
----------
⇒ Stimule la sécrétion de GH
⇒ Régule la fonction gonadotrope hypophysaire
(LH, FSH)
⇒ Inhibe sécrétion de Prolactine, GHRH et GH
⇒ Régulation de l’appétit
Périventriculaire • Somatostatine ⇒ Idem supra
Ventral • GHRH, Somatostatine
----------
⇒ Idem supra
⇒ Centre de la satiété
Latéral ---------- ⇒ Centre de la faim
Antérieur ---------- ⇒ Thermorégulation (thermolyse)
⇒ Centre de la soif (plancher du V3)
Postérieur ---------- ⇒ Thermorégulation (thermogenèse)
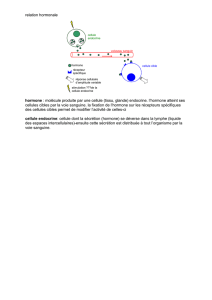
NEUROHORMONES HYPOTHALAMIQUES
NEUROHORMONES HYPOTHALAMIQUES
Nom Français Appellation Internationale Abr. Nature Biochimique
Corticolibérine Corticotropin-releasing
hormone CRH polypeptide (41 aa)
Thyréolibérine Thyrotropin-releasing
hormone TRH tripeptide (3 aa)
Gonadolibérine Gonadotropin-releasing
hormone GnRH decapeptide (10 aa)
Somatolibérine Growth hormone-
releasing hormone GRH
(GHRH) polypeptide (44 aa)
Somatostatine Growth hormone-
inhibiting hormone,
Somatostatin
GIH SS
(SRIF)
polypeptide (14 aa)
Dopamine Prolactin-inhibiting
hormone PIH Dopamine Dopamine
Prolactolibérine Prolactin-releasing factor PRF polypeptide
Les principales hormones hypothalamiques (libérines et statines) :

Physiologie Endocrine
Appareil Hypothalamo-Hypophysaire
4
NEURO
NEURO-
-HORMONES HYPOTHALAMIQUES
HORMONES HYPOTHALAMIQUES
Hypothalamus Tige pituitaire Post-hypophyse
Arginine Vasopressine
(AVP ou ADH)
Ocytocine
Pré-prohormone Prohormone + pept N-term
(copeptine pour ADH) Hormone + Neurophysine
(I = AVP, II = Ocy) + pept N-term
Cys–Tyr –Phe–Gln-Asn–Cys–Pro –Arg–Gly–NH
2
S S
Cys–Tyr –Ile –Gln-Asn–Cys–Pro –Leu – Gly – NH2
S S
OCYTOCINE
OCYTOCINE
Caractéristiques
-9 AA dont 2 différents de l’ADH
- Demi-vie : 3 – 5 min
- Dégradation : foie et reins (± myomètre et glandes mammaires)
- Agit via récepteur RCPG couplé à PLC (action pro-contractile
sur fml de l’utérus et cellules myo-épithéliales des glandes
mammaires)
Cys–Tyr –Ile –Gln-Asn–Cys–Pro –Leu – Gly – NH2
S S

Physiologie Endocrine
Appareil Hypothalamo-Hypophysaire
5
ACTIONS DE L
ACTIONS DE L’
’OCYTOCINE
OCYTOCINE
Implications pathologiques
Inhibée par stress et douleur (Pb lors de l’allaitement)
Déficit : travail et éjection du lait plus difficiles mais possibles
Stimulation per-coïtal : contractions utérines douloureuses en post-coïtal
Lactation
Stimulation : allaitement (stimuli psychiques) et succion du mamelon
(réflexe neuro-hormonal)
Action : contraction cell. myoépithéliales (alvéoles glandes mammaires)
Effet : éjection du lait (± effet anti-natriurétique et anti-diurétique modéré)
Motricité utérine
Stimulation:étirement col utérin + partie haute vagin
Action : contraction myomètre (↑par oestradiol et ↓par progestérone),
Effets : accouchement = travail (ne le déclenche pas physiologiquement),
limite hémorragie post-partum, contribue à l’orgasme et migration sperme
HYPOTHALAMUS et HYPOPHYSE POSTERIEURE
D – L’HORMONE ANTI-DIURÉTIQUE
1 - Actions du récepteur V2 : régulation de l’homéostasie
hydrique
a - Action rénale
b - Effet dipsogène
2 - Actions du récepteur V1
a - Actions rénales
b - Action vasculaire systémique
c - Action hypophysaire
3 - Contrôle de la sécrétion
a – Osmotique
b – Volémique
c - Interaction entre contrôles osmotique et volémique
d - Autres facteurs
4 – La soif
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
1
/
11
100%
![pathologie hypophysaire 2016 [Mode de compatibilité]](http://s1.studylibfr.com/store/data/000333899_1-48eb3fbed22db589999bffff6e4e4ee2-300x300.png)