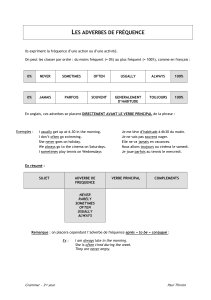
Present simple ou Present be+ing

Present simple ou Present be+ing
Choose the right tense between the two presents.
Exercise 1
1. Joan (play) football every day.
Joan plays football every day.
2. Who (walk) on the grass?
Who is walking on the grass?
3. We always speak softly while Mother (sleep).
We always speak softly while Mother sleeps.
4. Who (talk) you to?
Whom are you talking to?
5. Jim says: “I (go) to school now.”
jim says: “I am going to school now.”
6. In the winter, the sun (set) early.
In the winter, the sun sets early.
7. The church bell (ring) for Mass every Sunday.
The church bell rings for Mass every Sunday.
8. (Listen) you to me? I (not go) to repeat myself.
Are you listening to me? I am not going to repeat myself.
9. I (not remember) his name.
I do not remember his name.
10. No, I (not sleep); I am awake.
No, I am not sleeping ; I am awake.
Exercise 2
1. It is 7.30 a.m. and I (have) my breakfast.
It is 7.30 am and I am having my breakfast. (il dit une heure puis explique ce qu'il est en
train de faire.)
2. Every morning, at 7.30 a.m., I (have) breakfast.
Every morning, at 7.30 am, I have breakfast. (expression d'habitude)
3. At the moment, it (rain).
At the moment, it is raining. (“en ce moment”)
4. (Watch) you TV in the evening?
Do you watch TV in the evening? (“le soir”, expression d'habitude)
5. What (do) John right now?
What is John doing right now? (“maintenant”)
6. Quiet please! (Know) you how late it is?

Quiet please! Do you know how late it is? (“silence SVP”, en train de se dérouler)
7. Look! The police (arrest) someone next door.
Look! The police is/are arresting someone next door. (possiblité de mettre le verbe au
singulier si l'on fait référence à LA police en tant qu'entité, comme LA marine ou LE
gouvernement par exemple. Au pluriel si l'on fait référence aux policiers qui composent la
brigade qui intervient)
8. (Promise) you to be on time? Yes, I promise.
Do you promise to be on time? Yes, I promise. (une promesse est un engagement qui ne
peut durer que sur l'instant, donc présent simple)
9. What is that noise? (hit) Someone the wall?
What is that noise? Is someone hitting the wall? (perception d'un bruit donc prueve que cela
se passe en ce moment)
10. (Understand) you what I mean?
Do you understand what I mean? (Comprendre quelque chose ne peut se réaliser que sur
l'instant d'où le présent simple)
Exercise 3
1. She (not understand) much.
She does not understand much. (voir ci-dessus)
2. Driving (get) impossible!
Driving is getting impossible. (“conduire devient impossible” ne se comprend que dans le
déroulement de ce processus.)
3. Dad (clean) his car again!
Dad is cleaning his car again! (valeur de commentaire du présent be+ing, vue en cours.)
4. It (snow) often in winter.
It often snows in winter. (habitude traduite par often, souvent)
5. She (give) me pocket-money every Sunday.
She gives me pocket-money every Sunday. (expression d'habitude)
6. Look! He (push) her!
Look! He is pushing her! (“regarde”)
7. She (call) sometimes a taxi to go shopping.
She sometimes call a taxi to go shopping. (expression d'habitude avec sometimes, parfois)
8. Look! They (cross) the street without watching out.
Look! They are crossing the street without watching out. (“regarde”)
9. Why (make) you an apple-pie?
Why are you making an apple-pie? (sans contexte, le fait de poser cette question implique
que cela se passe sous les yeux du locuteur.)
10. Dad (not go) often to meetings.

Dad does not often go to meetings. (expression d'habitude)
1
/
3
100%




![[ʃeəd] Je raconte ce que j`ai fait pendant les vacances de Noël](http://s1.studylibfr.com/store/data/001164905_1-2e6cfa90f77742ecc6b3324739706198-300x300.png)




