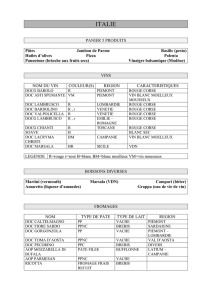
malformations de l`oreille interne

MALFORMATIONS DE
L'OREILLE INTERNE
Rappel embryologique (Pearson, 1979)
€Neurectoderme : v•sicule otique, labyrinthe
membraneux
€MÄsoblaste : labyrinthe osseux, platine
•trier, espaces p•ri lymphatiques
€I, IIes poches entoblastiques : trompe
eustache, cavit• tympanique, attique,
cavit•s post.
€Ier arc branchial : marteau (t‚te, col),
enclume (corps, courte apophyse)
€IIiÅme arc branchial : •trier, longue
apophyse enclume
SFR Languedoc Roussillon

MALFORMATIONS DU
LABYRINTHE OSSEUX
CLASSIFICATION (Jackler. 1987)
I -CochlÄe absente ou mal formÄe
ƒAplasie labyrinthique compl„te (type Michel)
ƒAplasie cochl•aire
ƒHypoplasie cochl•aire
ƒCochl•e mal form•e (Mondini)
ƒV•sicule unique : cochl•e et vestibule fusionn•s canaux normaux ou
mal form•s
II -Malformations avec cochlÄe normale
ƒDysplasie vestibule + C.S. externe
ƒ Dilatation de l'aqueduc du vestibule, canaux normaux, vestibule
normal ou dilat•
SFR Languedoc Roussillon

DILATATION AQUEDUC VESTIBULE
SFR Languedoc Roussillon

DYSPLASIE CSL -VESTIBULE
SFR Languedoc Roussillon

DYSPLASIE CSL -VESTIBULE
SFR Languedoc Roussillon
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
1
/
32
100%