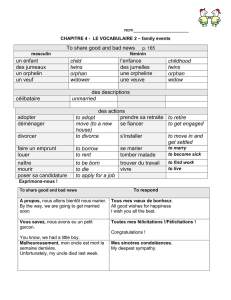
Le Verbe Devoir Devoir is a useful verb whose meaning can change

Le Verbe Devoir
Devoir is a useful verb whose meaning can change depending on the context.
First, let’s look at the conjugations:
Le présent
Je dois
Tu dois
Il doit
Nous devons
Vous devez
Ils doivent
Passé Composé
J’ai dû
Tu as dû
Il a dû
Nous avons dû
Vous avez dû
Ils ont dû
L’imparfait
Je devais
Tu devais
Il devait
Nous devions
Vous deviez
Ils devaient
Le futur
Je devrai
Tu devras
Il devra
Nous devrons
Vous devrez
Ils devront
Conditionnel
Je devrais
Tu devrais
Il devrait
Nous devrions
Vous devriez
Ils devraient
Conditionnel passé
J’aurais dû
Tu aurais dû
Il aurait dû
Nous aurions dû
Vous auriez dû
Ils auraient dû
The different meanings of devoir :
1. If devoir is used alone as the main verb in a sentence, it has the sense of “to
owe”
2. If it is used along with another verb, it has the sense of “must” (probably),
to be supposed to, to be expected to, should/ought to.
It is the verb tense that determines the meaning.
Look at the chart on the next page :

Tense
Meaning
Example
Present/
imperfect
Must
Il doit faire froid en Alaska.
Is supposed to
Luc doit téléphoner à Caroline cette semaine.
Was supposed to
Il devait lui téléphoner la semaine dernière.
Future
Will be expected to/
will have to
Dans cette classe, on devra parler français.
Passé composé
Must have
J’ai dû laissé mes papiers chez moi.
Conditional
Should
Je devrais étudier davantage.
Conditionnel passé
Should have
J’aurais dû écrire cette lettre hier.
Il faut has only one sense « to have to »
Be careful, however, because the negative form “il ne faut pas” means “must
not”
1
/
2
100%