Etude d`incidence des cancers éligibles pour une hadronthérapie

L’étude EpiHadron
Etude d’incidence auprès de la population de la région Rhône-
Alpes atteinte de cancers pour lesquels un traitement est
proposé en hadronthérapie par protons ou ions carbone.
METHODOLOGIE

Contexte
-PNRH : Programme National de Recherche en Hadronthérapie
-Le GCS ETOILE : groupement des CHU et CRLCC Rhône Alpes : ouvert en 2008 pour la
construction et exploitation du centre nationale de carbone thérapie
-Financement par L’Inca dès 2008 d’OMéRRIC: Organisation Médicale pour le
Recrutement des patients pour une Radiothérapie par Ions Carbone
- Réponse au Plan cancer et thématique cancéropole R. Alpes le CLARA

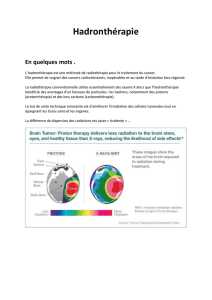
La carbone thérapie en bref
Précision balistique avec dépôt de la
dose au cœur de la tumeur Une efficacité biologique anti-tumorale (1.5 à 3 fois
supérieure) aux photons, électrons et aux protons
Gains pour le patient !
Cliniques: conserve les tissus sains autour de la tumeur
Conservateur : préserve l’intégrité physique du patient ( tumeur inopérables)
Qualité de vie: réduction des effets secondaires et du risque de séquelles

Adenoid Cystic carcinoma of maxillary sinus
(Pr Tsujii, NIRS)

Problématique
- Peu de données épidémiologiques disponibles concernant l’hadronthérapie
- Aucune information dans les registres de cancer
- Une demande de soin en augmentation
Nécessité de réaliser une évaluation de la demande de soin
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
1
/
24
100%