Unit in Biomedical Research in Urology resistance in aggressive prostate cancer VHIR

VHIR
Unit in Biomedical Research in Urology
In search for good therapeutic targets to annihilate the
resistance in aggressive prostate cancer

VHIR
· To identify PCa markers helpful for the diagnosis and prognosis of the aggressive
disease.
· To understand the mechanisms implicated in PCa progression to a resistant disease.
This may lead to discover more efficient therapeutic targets to eliminate the recurrent
metastatic cancer.
_________________________________
•Discovery of the oncoprotein PTOV1, hints about its function and mechanisms of action in
aggressive PCa, and in the resistance to chemotherapy.
•Models systems to study in vitro the biology of PCa and their response to treatments.
Major aims of our research

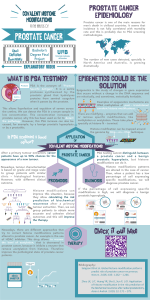
VHIR PROSTATE CANCER
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015
-Most common neoplasia among males in the western
Countries.
-Second leading cause of death from cancer in men.
Efforts and therapeutic strategies are focused on the
metastatic disease which almost invariantly becomes
recurrent and incurable
PROSTATE CANCER – DEVELOPMENT AND METASTASIS
5-year survival (%)
Survival (%)

VHIR
Androgen sensitive Androgen resistant
Therapeutic approaches for Prostate Cancer progression
ADT

VHIR
Localized Tumor Metastasis
Pre-malignant
(HG-PIN)
Localized Tumor
Normal Prostate
Pérdida de células
basales
Pérdida de lámina
basal
Andrógeno-independencia
HG-PIN
Normal Epithelia
Androgen-independent
Progression of human Prostate Cancer
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
1
/
42
100%