UNIVERSITE ABOU BEKR BELKAID - TLEMCEN

REPUBLIQUE ALGERIENNE DEMOCRATIQUE ET POPULAIRE
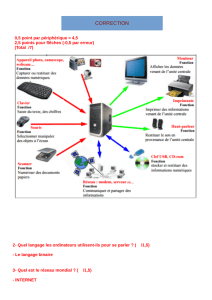
MINISTERE DE L’ENSEIGNEMENT SUPERIEUR
ET DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
UNIVERSITE ABOU BEKR BELKAID - TLEMCEN
FACULTE DE TECHNOLOGIE
DEPARTEMENT DU GENIE ELECTRIQUE ET ELECTRONIQUE
LABORATOIRE DE TELECOMMUNICATIONS
MEMOIRE
Pour l’obtention du
DIPLOME DE MAGISTER EN TELECOMMUNICATIONS
MEDJDOUB Fadila
Optimisation par la simulation système d’une
chaine de transmission numérique par fibre
optique haut débit
Soutenu en 2010 devant le jury:
Président : O. SEDDIKI Professeur à l’Université de Tlemcen
Examinatrice : F.Z BENMANSOUR Maître de conférences à l’Univ. de Tlemcen
Examinateur : S.M MERIAH Maître de conférences à l’Univ. de Tlemcen
Examinateur : N. BOUkLI HACENE Maître de conférences à l’Univ. de Tlemcen
Encadreur : M.CHIKH BLED Professeur à l’Université de Tlemcen
Année universitaire 2009-2010.

A mes très chers parents
Merci

Remerciement
Avant tout, je remercie le BON DIEU de m’avoir aidé à réaliser
ce présent travail.
J’adresse tout particulièrement à Mr « M. CHIKH-BLED »,
Professeur à l’Université Abou-Bakr Belkaid, mes sincères
reconnaissances et mes remerciements les plus vifs, de m’avoir
dirigé et guidé tout le long de ce travail. Ses critiques constructives,
remarques et précieux conseils ont contribué à faire progresser mes
recherches.
J’exprime ma gratitude à Mr « O.SEDDIKI », Professeur à
l’Université Abou-Bakr Belkaid, qui a bien voulu me faire l’honneur
de présider le jury de cette thèse.
Je tiens à exprimer également mes remerciements à
Me « F.Z BENMANSOUR », Maître de conférences à l’Université
Abou-Bakr Belkaid, d’avoir bien voulu accepter d’être membre de
jury.
A Mr « S.M.MERIAH » et Mr « N. BOUKLI HACENE »,
Maîtres de conférences à l’Université Abou-Bakr Belkaid, qu’ils
veillent bien trouver l’expression de mes profondes reconnaissances
d’avoir voulu malgré les tâches qui les accaparent de faire jury.
Mes respectueux remerciements vont à tous les membres du
laboratoire de Télécommunication de la Faculté des Sciences de
l’Ingénieur où ce travail a été effectué, pour leurs conseils, leur
soutien et l’ambiance de travail qu’ils nous ont su créés.
Enfin, j’adresse mes remerciements les plus distinguées à mes
chers parents dont le soutien aussi bien moral que matériel ne m’a
jamais fait défaut.

Résumé :
Le haut débit, la grande distance de propagation et la bonne qualité de transmission
combinés à un coût réduit sont des critères de plus en plus demandés pour la réalisation
d’un système de télécommunications. Un compromis entre ces divers critères ne peut se
faire que si un système de transmission optique est mis en jeu avec ses propres composants
dont les caractéristiques sont bien spécifiées.
Notre travail consiste à trouver ce compromis en choisissant les composants
convenables pour la conception d’une chaine de transmission à 40 Gb/s après avoir
effectué une étude bien détaillée des modèles utilisables. La liaison conçue présente
comme toute chaine de télécommunication des inconvénients qui influencent la
propagation du signal le long de la fibre. Ce sont les effets linéaires et non linéaires qui
doivent être éliminés ou plus au moins limités en introduisant des techniques spéciales
telles que la compensation de dispersion et l’amplification.
La partie simulation de ce mémoire fait appel au logiciel COMSIS qui nous donne
la possibilité de concevoir des chaines comparables à ceux existantes dans la réalité, avec
visualisation des performances à l’aide du facteur de qualité et du taux d’erreur binaire.
Abstract:
The high flow, the long distance of propagation and the good quality of
transmission combined at a reduced cost are criteria increasingly required for the
realization of a system of telecommunications. A compromise between these various
criteria can be made only if one system of optical transmission is involved with its own
components whose characteristics are well specified.
Our work consists in finding this compromise by choosing the components suitable
for the design of transmission chains to 40 Gb/s after having carried out a well detailed
study of the models usable. The conceived link is as any chains of telecommunication
present the disadvantage which influences the propagation of the signal along fiber. Those
are the linear and nonlinear effects which must be to eliminate or at least to limit by
introducing special techniques such as the compensation of dispersion and the
amplification of attenuation.
The simulation part of this memory calls upon the software COMSIS which gives
us the possibility of designing chains comparable with those existing in reality, with
visualization of the performances using the factor of quality and the binary error rate.

ﺺﻴﺨﻠﺗ
ﻲﻟﺎﻌﻟا ﻖﻓﺪﺘﻟا ,و ةﺮﻴﺒﻜﻟا لﺎﺳرﻹا ﺔﻓﺎﺴﻣ ﺔﻴﻋﻮﻨﻟا ﺮﻴﻳﺎﻌﻣ ﻲه ﺔﻀﻔﺨﻨﻣ ﺔﻔﻠﻜﺘﺑ ﺔﻧوﺮﻘﻣ ﺔﻣﻮﻠﻌﻤﻟا لﺎﻘﺘﻧﻻ ةﺪﻴﺠﻟا
ﺔﻴﻜﻠﺳﻼﻟا و ﺔﻴﻜﻠﺴﻟا تﻻﺎﺼﺗﻻا مﺎﻈﻧ ﻖﻠﺨﻟ ﺪﻳاﺰﺘﻣ ﻮﺤﻧ ﻰﻠﻋ ﺔﺑﻮﻠﻄﻣ.
ﺔﺻﺎﺨﻟا ﻪﺗﺎﻧﻮﻜﻤﺑ يﺮﺼﺑ ﺚﺑ مﺎﻈﻧ دﻮﺟﻮﺑ ﻻإ ﺮﻴﻳﺎﻌﻤﻟا ﻩﺪه ﻒﻠﺘﺨﻣ ﻦﻴﺑ ﻂﺳو ﻞﺣ ﻖﻴﻘﺤﺗ ﻦﻜﻤﻳ ﻻ ﻢﻟﺎﻌﻤﻟا تاذ
ةدﺪﺤﻤﻟا.
يﺮﺼﺑ ﺚﺑ ﺔﻠﺴﻠﺳ ﻢﻴﻤﺼﺗ ﻞﺟا ﻦﻣ ﺔﺒﺳﺎﻨﻤﻟا ﺮﺻﺎﻨﻌﻟا رﺎﻴﺘﺧﺎﺑ ﻞﺤﻟا اﺪه دﺎﺠﻳإ ﻲﻓ ﻦﻤﻜﺗ ﺎﻨﺘﻤﻬﻣ40 ﺖﺑ ﺎﺠﻴﺟ
ﺔﻠﻤﻌﺘﺴﻤﻟا جذﺎﻤﻨﻟا ﻦﻋ ﺔﻠﺼﻔﻣ ﺔﺳارد ءاﺮﺟإ ﺪﻌﺑ ﺔﻴﻧﺎﺜﻟا ﻲﻓ.
ﻲﻓ ﺎهروﺮﻣ ىﺪﻟ ﺔﻣﻮﻠﻌﻤﻟ ارﺎﺸﺘﻧا ﻰﻠﻋ ﺮﺛﺆﺗ ﻲﺘﻟا ﺎﻬﺑﻮﻴﻋ ﺎﻬﻟ تﻻﺎﺼﺗا ﺔﻠﺴﻠﺳ ﻞﻜآ و ﺔﻠﺴﻠﺴﻟا ﻩﺪه فﺎﻴﻟﻷا
ﺔﻳﺮﺼﺒﻟا . تﺎﻴﻨﻘﺗ ماﺪﺨﺘﺳا ﻖﻳﺮﻃ ﻦﻋ ﺎﻬﻨﻣ ﺪﺤﻟا ﻞﻗﻷا ﻰﻠﻋ وأ ﺎﻬﻴﻠﻋ ءﺎﻀﻘﻟا ﺐﺠﻳ ﻲﺘﻟا ﺔﻴﻄﺨﻟا ﺮﻴﻏ و ﺔﻴﻄﺨﻟا رﺎﺛﻵا ﺎﻬﻧإ
ﺺﻗﺎﻨﺘﻟا ﻢﻴﺨﻀﺗو رﺎﺸﺘﻧﻻا ﺾﻳﻮﻌﺘﻟ ﺔﺻﺎﺧ .
ﻚﻠﺘﻟ ﺔﻬﺑﺎﺸﻣ ﻞﺳﻼﺳ ﻢﻴﻤﺼﺘﻟ ﺔﺻﺮﻔﻟا ﺎﻨﻟ ﺢﻴﺘﻳ ىﺪﻟأ COMSIS ﺞﻣﺎﻧﺮﺑ مﺪﺨﺘﺴﻳ ﻲﻘﻴﺒﻄﺘﻟا ﻞﻤﻌﻠﻟ ﺺﺼﺨﻤﻟا ءﺰﺠﻟا
ﻤﻟاﺄﻄﺨﻟا لﺪﻌﻣ و ةدﻮﺠﻟا ﻞﻣﺎﻋ ةﺪﻋﺎﺴﻤﺑ ةدﻮﺠﻟا ﺔﻓﺮﻌﻣ ﺔﻴﻧﺎﻜﻣإ ﻊﻣ ﻊﻗاﻮﻟا ﻲﻓ ةدﻮﺟﻮ.
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
 45
45
 46
46
 47
47
 48
48
 49
49
 50
50
 51
51
 52
52
 53
53
 54
54
 55
55
 56
56
 57
57
 58
58
 59
59
 60
60
 61
61
 62
62
 63
63
 64
64
 65
65
 66
66
 67
67
 68
68
 69
69
 70
70
 71
71
 72
72
 73
73
 74
74
 75
75
 76
76
 77
77
 78
78
 79
79
 80
80
 81
81
 82
82
 83
83
 84
84
 85
85
 86
86
 87
87
 88
88
 89
89
 90
90
 91
91
 92
92
 93
93
 94
94
 95
95
 96
96
 97
97
 98
98
 99
99
 100
100
 101
101
 102
102
 103
103
 104
104
 105
105
 106
106
 107
107
 108
108
 109
109
 110
110
 111
111
 112
112
 113
113
 114
114
 115
115
 116
116
 117
117
 118
118
 119
119
 120
120
 121
121
 122
122
 123
123
 124
124
 125
125
 126
126
 127
127
 128
128
 129
129
 130
130
 131
131
 132
132
 133
133
 134
134
 135
135
 136
136
 137
137
 138
138
 139
139
 140
140
 141
141
 142
142
 143
143
 144
144
 145
145
 146
146
 147
147
 148
148
 149
149
 150
150
 151
151
1
/
151
100%