La construction de l`interrogatif et du négatif

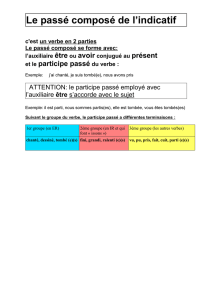
La construction de l’interrogatif
L’interrogatif en anglais exige l’utilisation d’un verbe auxiliaire. Sont considérés comme
verbes auxiliaires :
Be, have, do, will, shall, would, can, could, may, might, should, must, need.
Pour construire l’interrogatif en anglais on utilise une méthode logique en trois étapes.
Étape 1
Est-ce que le verbe principal de la phrase est ‘To Be’?
Non: passez à l’étape 2
Oui: inversez le sujet et le verbe. Le reste de la phrase ne change pas.
Ex. He is the managing director of the company.
Sujet + to be + complément
Is he the managing director of the company?
To be + sujet + complément
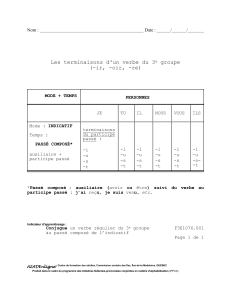
Étape 2
La phrase contient-elle un verbe auxiliaire?
Non: Passez à l’étape 3
Oui: inversez le sujet et le verbe auxiliaire. Le reste de la phrase ne change pas..
Ex. . He will fire his personal assistant next week.
Sujet + auxiliaire + verbe + complément
Will he fire his personal assistant next week?
Auxiliaire + sujet + verbe + complément
We are going to the cinema tonight
Sujet + auxiliaire + verbe + complément
Are we going to the cinema tonight ?
Auxiliaire + sujet + verbe + complément

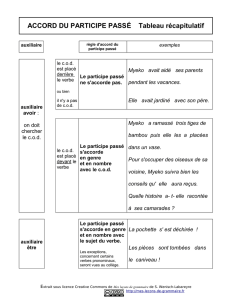
Etape 3
Si le verbe principal de la phrase n’est pas ‘to be’ et que la phrase ne contient pas
d’auxiliaire, la forme appropriée de l’auxiliaire ‘to do’ (do/does/did) doit être introduite dans
la phrase. Ensuite, inversez le sujet et l’auxiliaire et mettez l’infinitif du verbe principal après
le sujet.
Note : Have n’est pas considéré comme verbe auxiliaire quand il signifie “avoir”.
TO DO’ (DO/DOES/DID)+SUJECT+INFINITIVE + COMPLEMENT
The workers come to the factory every day.
Sujet + verbe + complément
Do the workers come to the factory every day ?
Auxiliaire + sujet + verbe + complément
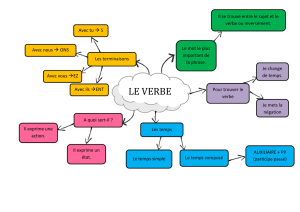
Si la phrase contient un mot question (what, why, how etc), il se place devant l’auxiliaire.
Mot question
Auxiliaire
Sujet
Verbe
Complément
Do
you
work
on Mondays
Where
does
he
work?
Where
am
I
working
today?
Who
is
he
working
for?
Are
we
working
today?
Did
you
work
yesterday?
Why
were
they
working
at lunchtime?
Who
was
he
working
with?
Has
she
worked
all morning?
Have
they
worked
today?
How long
has
he
been working?
What
have
you
been working
on?
How long
had
we
worked?
When
had
it
been working?
When
will
you
work
on this project?
Will
he
have been working
for long?
Why
would
she
work
with him?
Shall
we
work
together?
Can
we
work
in a team?
Who
could
they
work
with?
Which project
should
he
work
on?
Must
I
work
today
May
she
work
with me?
Might
it
work
tomorrow?
Need
she
work
next week?

La construction du négatif
Le négatif en anglais exige l’utilisation d’un verbe auxiliaire. Sont considéré comme
verbes auxiliaires :
Be, have, do, will shall, would, can, could, may, might, should, must, need.
Pour construire le négatif en anglais on utilise une méthode logique en trois étapes.
Étape 1
Est-ce que le verbe principal de la phrase est ‘To Be’?
Non: passez à l’étape 2
Oui: ajoutez NOT après l’auxiliaire. Le reste de la phrase ne change pas.
Ex. He is the managing director of the company.
Sujet + to be + complément
He is not the managing director of the company.
Sujet + to be + NOT + complément
Étape 2
La phrase contient-elle un verbe auxiliaire?
Non: passez à l’étape 3
Oui: ajoutez NOT après l’auxiliaire. Le reste de la phrase ne change pas..
Ex. . He will fire his personal assistant next week.
Sujet + auxiliaire + verbe + complément
He will not fire his personal assistant next week.
Sujet + auxiliaire + not + verbe + complément
We are going to the cinema tonight
Sujet + auxiliaire + verbe + complément
We are not going to the cinema tonight ?
Sujet + auxiliaire + not + verbe + complément
1
/
3
100%