sequence 03

SEQUENCE 03
LES TROIS FONCTIONS ECONOMIQUES
LA PRODUCTION ET LE SYSTEME PRODUCTIF......................................................................................40
INTRODUCTION .......................................................................................................................40
I. LA PRODUCTION MARCHANDE ET LA PRODUCTION NON MARCHANDE....41
A. LA PRODUCTION......................................................................................................................41
1. La définition de la production par l’INSEE..........................................................................41
2. Typologie des biens produits.................................................................................................41
B. LA PRODUCTION MARCHANDE..........................................................................................42
1. Définition ................................................................................................................................42
2. Schéma de synthèse................................................................................................................42
C. LA PRODUCTION NON MARCHANDE ET L’INTERVENTION DE L’ETAT
DANS LA PRODUCTION..........................................................................................................42
1. Définition ................................................................................................................................42
2. La notion de services publics.................................................................................................42
3. Le cas particulier de la France : de la nationalisation à la libéralisation.............................44
4. Schéma de synthèse................................................................................................................45
II. LA MESURE DE LA RICHESSE ET SES LIMITES .....................................................45
A. LA RICHESSE CREEE PAR L’ENTREPRISE EST LA VALEUR AJOUTEE....................45
1. La notion de valeur ajoutée....................................................................................................45
2. Le calcul de la valeur ajoutée.................................................................................................47
3. Comment est répartie la valeur ajoutée ? ..............................................................................47
B. LA SOMME DES VALEURS AJOUTEES CORRESPOND DONC A LA
RICHESSE CREEE SUR UN TERRITOIRE............................................................................48
1. L’intérêt de la notion de valeur ajoutée pour calculer le PIB..............................................48
2. Schéma de synthèse................................................................................................................49
C. LA MESURE DE LA PRODUCTION PAR LE PIB ET SES LIMITES................................49
1. Le PIB......................................................................................................................................49
2. Les limites de la mesure de la richesse par PIB....................................................................52
3. La prise en compte des limites du PIB : l’Indice de Développement Humain...................52
4. Schéma de synthèse : les limites de la mesure de la production .........................................53
D. LES AUTRES AGREGATS DE MESURE DE RICHESSE D’UNE NATION.....................53
1. Qu’est-ce qu’un agrégat ? ......................................................................................................53
2. Les principaux agrégats de mesure de richesse....................................................................53
III. LE SYSTEME PRODUCTIF.............................................................................................54
A. CARACTERISTIQUES DU SYSTEME PRODUCTIF ...........................................................54
1. Les 3 grands secteurs..............................................................................................................54
2. Les branches et les filières .....................................................................................................56
B. LA STRUCTURE DU MARCHE...............................................................................................57
1. Concurrence, oligopole, monopole........................................................................................57
2. Processus de concentration pour modifier la structure du marché......................................57
C. L’INTERNATIONALISATION DU SYSTEME PRODUCTIF..............................................57
1. La réalité et les causes de l’internationalisation des entreprises..........................................57
2. Les délocalisations..................................................................................................................58
CONCLUSION DE LA SEQUENCE........................................................................................60

SEQUENCE 03
8 3506 TG PA 00 40
LES TROIS FONCTIONS ECONOMIQUES
LA PRODUCTION ET LE SYSTEME PRODUCTIF
Objectifs
1. Distinguer les notions de production marchande et non marchande et montrer le rôle de l’État
et du secteur public productif. (I) (1 h)
2. Définir les principaux agrégats de la comptabilité nationale et repérer les limites de la mesure
de la production. (II) (1 h 30)
3. Définir les notions de secteurs et de branches, repérer leur évolution et mettre en évidence
l’internationalisation de la production. (III) (1 h 30)
MOTS CLEFS
Partie I : Production marchande et non marchande, biens de consommation et de production, services
publics.
Partie II : Valeur ajoutée, produit intérieur brut, agrégat.
Partie III : Système productif, secteurs économiques, branches, filières, structure du marché,
internationalisation du système productif.
INTRODUCTION
Entrée en matière : Nous avons vu au cours de la séquence 01 que la consommation de biens nous
permettait de satisfaire nos besoins. Or, comme le dit si bien Fourastié, « nous travaillons pour produire
afin de pouvoir consommer » car, à l’état brut, la nature est « une dure marâtre pour l’humanité ».
Définition et intérêt du sujet : Produire, c’est créer des biens qui ne sont pas naturellement et
immédiatement disponibles. Nous verrons qu’il y a une typologie des biens produits et que la production est
une activité économique organisée pour créer des biens et services.
Problématique : Comment est organisée la production, donc le système productif ?
Plan : Pour y répondre, nous verrons :
– une définition complète de la production en présentant la production marchande sans négliger
l’importance de la production non marchande (I).
– que la production est la fonction économique de base pour créer, mesurer la richesse par le PIB, et ce
malgré certaines controverses (II).
– comment est concrètement organisée et répartie la production. C’est le système productif (III).

SEQUENCE 03
8 3506 TG PA 00 41
I. LA PRODUCTION MARCHANDE ET LA PRODUCTION NON
MARCHANDE
A. LA PRODUCTION
1. La définition de la production par l’Insee
« La production est l’activité économique socialement organisée consistant à créer des biens et
services s’échangeant habituellement sur le marché ou obtenus à partir de facteurs de production
s’échangeant sur le marché. »
Cela signifie que la production est une création du travail humain pour proposer des biens de
consommation et de production. Cette organisation du travail humain combine donc les facteurs de
production (nous verrons au cours des séquences 04 et 05 que ce sont le travail rémunéré et les machines).
Mais attention : seules les activités qui donnent lieu à un travail rémunéré sont considérées comme des
productions. Ainsi tous les travaux domestiques, d’éducation des enfants et d’entraide ne sont pas considérés
comme des activités productives. Cependant, on distingue la production marchande et la production non
marchande.
2. Typologie des biens produits
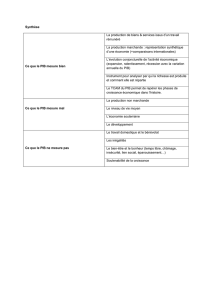
Question
Trouvez un exemple pour chacun des types de produits énoncés sur la droite du schéma.
Les différents types de produits
Marc MONTOUSSÉ,
« Comprendre l’économie, concepts et mécanismes », Cahiers français, n° 315, p. 24
Le fonctionnement de l’économie, la production, fruit du capital et du travail

SEQUENCE 03
8 3506 TG PA 00 42
Réponse
Biens de consommation
– biens durables : une maison ou un livre,
– biens non durables : une orange ou un cours,
– services marchands : une nuit d’hôtel ou une heure de leçon de conduite,
– services non marchands : un cours à l’école ou un match organisé par un club.
Biens de production
– biens intermédiaires : des planches de bois pour une table ou un processeur d’ordinateur,
– services intermédiaires : un service de maintenance pour l’entretien des machines ou un service
d’ingénierie,
– biens d’équipement : une fraiseuse ou une chaîne de production,
– investissements immatériels : achat d’un brevet ou lancement d’un programme de recherche.
B. LA PRODUCTION MARCHANDE
1. Définition
La production marchande mesure la valeur des biens et services vendus sur le marché au prix qui couvre les
coûts de production.
La production marchande est mise sur le marché par les entreprises ; elle est surtout le fait des
entreprises qui mettent sur le marché près de 90 % de la production marchande vendue.
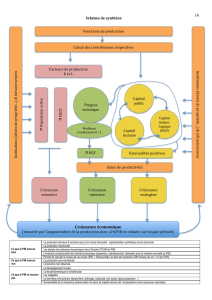
2. Schéma de synthèse
PRODUCTION MARCHANDE
– Création du travail humain par une
combinaison de facteurs de production
– Entreprises privées mais aussi
entreprises publiques
MARCHÉ DES BIENS ET SERVICES
– Échange de l’offre et de la demande
contre un prix
– Prix de vente supérieur au coût de
production
C. LA PRODUCTION NON MARCHANDE ET L’INTERVENTION DE L’ETAT DANS
LA PRODUCTION
1. Définition
Ce sont les biens proposés par les administrations gratuitement ou à un prix inférieur aux coûts de
production. Le plus souvent, ce sont des services qui sont proposés par l’État.
Par exemple, nous pouvons citer les services d’enseignement de l’Éducation nationale car il s’agit d’une
production réalisée par des salariés rémunérés.
2. La notion de services publics
Le service public regroupe les activités économiques d’intérêt général que gère l’État (communication,
énergies, transport).
L’État prend aussi en charge les biens indivisibles appelés aussi biens collectifs. Ce sont les biens dont la
consommation faite par un consommateur ne réduit pas ou n’interdit pas la consommation faite par un autre

SEQUENCE 03
8 3506 TG PA 00 43
consommateur. Ex. : l’éclairage public : nous pouvons tous profiter de l’éclairage public, la consommation
en éclairage d’un citoyen dans la rue ne fait en aucun cas de l’ombre à un autre citoyen. De plus, on ne peut
interdire à de nouveaux consommateurs citoyens de ne pas profiter de cet éclairage.
Question
Pour quelles raisons l’État gère-t-il les services publics ? (réponse succincte)
Le service public repose sur l’idée que le marché ou l’initiative privée ne peuvent pas satisfaire
dans de bonnes conditions des besoins aussi essentiels que la sécurité intérieure, la défense
nationale, la protection de l’environnement, la cohésion sociale et territoriale, ou, plus
généralement, les libertés de base. L’égalité des citoyens ne signifierait pas grand-chose si, malgré
le droit de vote reconnu à tous, certains Français, ne pouvant téléphoner, se déplacer ni se chauffer
normalement, se sentaient « exclus » par des tarifs trop élevés ou par l’insuffisance des
équipements et des infrastructures (habitations non raccordées au réseau téléphonique du fait de
leur isolement, par exemple). La « péréquation » des tarifs publics, qui consiste à fixer des prix
égaux pour différentes catégories d’usagers, indépendamment des coûts de revient, rend possible
l’égalité au quotidien et donne un sens aux libertés fondamentales.
Bien au-delà de la simple satisfaction des besoins individuels, le service public a donc aussi pour
mission de répondre à des besoins d’intérêt général, comme le sentiment d’appartenir à une nation
et d’y être citoyen à part entière quels que soient son revenu, ses diplômes ou son lieu d’habitation.
De même, il permet théoriquement une meilleure utilisation des ressources humaines et matérielles
du pays grâce au réseau ferré, à la poste, aux hôpitaux, à l’état civil, au contrôle aérien, à
l’enseignement. Ces « biens communs » facilitent les initiatives individuelles, l’activité des
entreprises et, finalement, la croissance économique et l’emploi. Les enjeux sont là tellement
importants qu’ils relèvent de l’autorité publique.
Dictionnaire d’économie, Larousse et le Monde, p. 515
Votre réponse
Réponse
– Le marché est défaillant pour assurer l’égalité des citoyens quant à la satisfaction de certains besoins : la
sécurité intérieure et extérieure, la protection de l’environnement, la cohésion sociale et territoriale, les
libertés fondamentales comme le droit à l’enseignement par exemple.
– Le service public répond mieux à la notion d’intérêt général, participe à la cohésion sociale et territoriale,
permettant ainsi une amélioration du niveau de vie économique et social.
– Les services publics concourent à une meilleure attractivité des territoires, donc à la création de richesses
par de nouvelles activités productives et à la croissance et à l’emploi.
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
1
/
22
100%