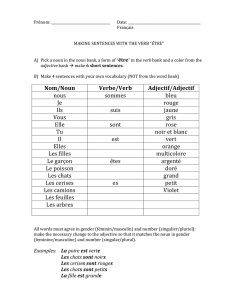
French Study Guide Superlative of Adjectives: Plus… (que) more

French Study Guide
Superlative of Adjectives:
Plus… (que) more… (than), … er (than)
Moins… (que) less… (than), not as… (as)
Aussi… (que) as… (as)
Le/la/les plus … the most
Le/la/les moins … the least …
Conjugations:
Present: Object pronoun is placed before the verb. Stem of the infinitive + the following
endings:
-er verbs
-e, -es, -e, -ions, -ez, -ent
-ir verbs
-is, -is, -it, -issons, -issez, -issent
-re verbs
-s, -s, - , -ons, -ez, -ent
Ex. Tu aimes, elle finit, nous vendons
Futur proche: aller(conjugated) + infinitive
-Je vais, Tu vas, Il va, Nous allons, Vous allez, Ils vont
Ex. Je vais en acheter beaucoup. Ex. Vas-tu acheter pour le concert?
Imperfect: the stem of the first person plural of the present indicative (the ‘nous’ form minus
-ons) + the following endings:
-ais, -ais, -ait, -ions, -iez, -aient
Future: infinitive + the following endings:
-ai, -as, -a, -ons, -ez, -ont
Ex. J’aimerai, elle finira, vous vendrez
*Note*: the verbs ending in –re drop the final e of the infinitive.

Passé Composé: Object is placed before avoir/ être. Normally there is no agreement when
you use avoir unless the direct object comes before the verb.
Ex. Est-ce que vous avez fini vos devoirs?
-Oui, nous les avons finis.
*Note*: lui/leur = indirect objects (with people, there is no agreement)
Ex. Est-ce que vous avez parlé à vos amis?
-Oui, nous leur avons parlé
Imparfait: Direct object is placed before the verb.
Ex. Est-ce que tu avais des animaux domestiques quand tu étais petit?
-Oui, j’en avais deux or Non, je n’en avais pas
Conditional: infinitive + the following endings:
-ais, -ais, -ait, -ions, -iez, -aient
Note that verbs ending in –re drop the final e of the infinitive.
Ex. Il aimerait, vous finiriez, je vendrais
Present Tense (2 verbs): Object pronoun is placed before the infinitive.
Ex. Veux-tu aller à la bibliothèque avec moi?
-Oui, je veux y aller or Non, je ne veux pas y aller
Future & Conditional: to express future actions, use aller + infinitive.
Ex. Ils vont partir ce week-end. They are going to leave this weekend.
-The future tense in French is formed by adding the following endings to the infinitive: -ai,
-as, -a, -ons, -ez, -ont.
Ex. Parler – je parlerai nous parlerons, ils/elles parleront
-If the infinitive of the verb ends in –e, that –e is dropped before the future endings are
added.
Ex. Je rendrai (rendre)
There are some irregular stem verbs such as: Aller (to go) > j’irai & Avoir (to
have) > j’aurai
Ex. Nous aimions, je finisse, ils vendent

Object Pronouns:
-The direct object pronoun comes before the verb.
Ex. -Je l’écris demain I’m writing it tomorrow
-Je ne les aime pas du tout. I don’t like them at all.
Me le lui y en the verb
Te > la > leur > > >
Se les
Nous
Vous
Présent = devant le verbe
Future proche = devant l’infinitif
Passé Composé = devant le premier verbe
Imparfait = devant le verbe
-Only use lui/leur when it is indirect (à)
Ex. À ma mere = lui
-Only agree with verb when it’s le/la/les
-object pronouns go in front of avoir. When object pronoun is in front of avoir/être, it must
agree
Demonstrative Adjectives
Ce is often used to point out a particular person or thing, or person or things. It is followed
by the noun to which it refers and agrees in number and gender with that noun:
With a masculine singular noun: ce(cet) this/that
With a feminine singular noun: cette this/that
With a plural noun (masc. or fem.): ces these/those
Cet is used instead of ce in front of a masculine singular word that begins with a vowel or
silent h: cet été this summer cet hotel that hotel

Interrogative and Exclamatory Adjectives
a) Forms
Quel – (which, what) agrees in number and gender with the noun it refers to. It has four
forms:
With a masculine singular noun: quel?
With a feminine singular noun: quelle?
With a masculine plural noun: quels?
With a feminine plural noun : quelles ?
b) direct questions
Quel est votre passe-temps favori ? What is your favorite pastime ?
Quelle heure est-il ? What time is it ?
Quels jours as-tu de libres ? Which days have you got free ?
Quelles affaires comptes-tu prendre avec toi ? What/which things do you intend to take with
you ?
Interrogative Pronouns
These are:
Lequel/laquelle/lesquels/lesquelles? Which(one(s)) ?
Qui ? Who ?
Que ? What ?
Quoi ? What ?
1
/
4
100%