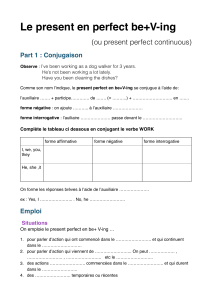
TENSE

TEMPS
FORMATION
Repères temporels
Emploi
EXEMPLES
PRESENT
SIMPLE
Aux: DO/ DOES
Formes: Aff:BV / BV-es
Int: (Wh-) Do / Does + S +V
Nég: S + do/does + not + BV
Everyday, every week,
month…
Always, usually, often,
never, sometimes…
(On) Mondays…
Habitude ou vérité
générale
Today I don’t feel like doing anything (Bruno Mars, the
lazy song)
What doesn’t kill you makes you stronger (Kelly
Clarkson)
I’m a Barbie girl (..), life in plastic, it’s fantastic (Aqua)
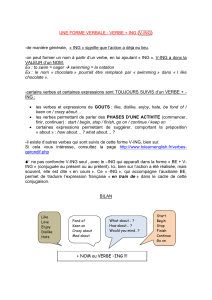
Le cas particulier de ‘used to’+ V-ing
Everyday, every …
Often, usually, always
au présent, il indique
une habitude, quelque
chose que l’on fait
sans problème
I’m used to working late at night.
PRESENT
CONTI
NUOUS
Aux: BE
Formes: Aff: I am
You /we /they are
He / she / it is
Int: (Wh-) Am/Is/Are + S + V-
ing
Nég: S + am/is/are+ not+ Ving
At the moment,
Now,
As we speak,
While,
when
Action ou situation
qui a lieu
simultanément au
moment de parole
(arrêt sur image) /
description
Like a hobo from a broken home, nothing’s going to stop
me (Charlie Winston, Like a hobo)
All the other boys are trying to chase me (Carly Ray
Jepsen, Call me maybe)
PRESENT
PERFECT
/
PRESENT
PERFECT
CONTI
NUOUS
Aux: HAS / HAVE
Formes: Aff: S +has/have + participe
passé
Int: (Wh-) Has/have + S + p.p.
Nég: S + has/have + not + p.p.
Aux : HAS / HAVE
Formes: Aff: S +has/have +been + pp
Int: (Wh-) Has/have + S + been
+ p.p.
Nég: S + has/have + not +been
+ p.p.
Already, ever, never,
Lately, recently,
So far,
Since, for
It’s the first time
Met l'accent sur le
résultat d'une action
dans le présent ou
permet de faire un
bilan
(V-ing): Insistance
sur la durée de
l'action, sur son
déroulement
Does it show again, (..) just how much I’ve missed you?
(Abba, Mamma mia)
I’ve been walking, I’ve been waiting, in the shadows
(The Rasmus, In the shadows)
I’ve been loving you too long (Otis Redding)
S= sujet BV= base verbale V-ing= verbe à la forme –ing p .p= participe passé
* l’emploi de l’auxiliaire + radical verbal à l’affirmatif est une forme d’insistance ex : She does like spinach ! C’est vrai qu’elle aime les épinards !
+ V-ing

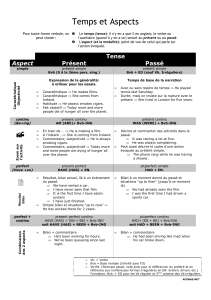
TEMPS
FORMATION
Repères temporels
Emploi
EXEMPLE
PAST
SIMPLE
(PRETERIT)
Aux: DID
Aff.: BV –ed / 2° forme des verbes
irréguliers
Nég.: S + did not (didn't) + BV
Int.: (Wh-) did +sujet + BV
Yesterday,
last week, month,
year, century…
in the past, formerly
… ago
Action ou situation passée,
repérée et terminée
He was a boy and she was a girl, can I make
it anymore obvious? (Avril Lavigne, Sk8ter
boI)
I heard that you found a girl (Adele,
Someone like you)
Why were they open? (Bruno Mars, Grenade)
But you didn’t have to cut me off (Gotie,
somebody that I used to know)
Le cas particulier de ‘used to’+ BV
Before, in my youth,
when I was…
au prétérit, il indique qq ch qui
était vrai dans le passé, mais ne
l’est plus au moment où l’on
parle
I used to rule the world, seas would rise
when I gave the word (Viva la Vida,
Coldplay)
PAST
CONTI
NUOUS
(PRETERIT
CONTI
NUOUS)
Aux: BE: was/were
Aff: Be au preterit (was/were) + V-ing
Nég: S + was/were +not + V-ing
Int: (Wh-) Was/Were + S +V-ing
Yesterday,
last week, month,
year, century…
in the past, formerly
while
when
Action ou situation révolue prise
dans son déroulement
(description par exemple)
I was walking with my mama one day when
she warned me what people say (Mika,
Lollipop)
PAST
PERFECT
(PLU
PERFECT)
/
PAST
PERFECT
CONTI
NUOUS
Aux: HAD
Aff: Had + p.p.
Nég: S + Had +not + p.p
Int: (Wh-) Had + S + p.p
Aff: Had + been +V-ing
Nég: S + had + been +not + V-ing
Int: had + S + been +V-ing
S'utilise pour faire référence à un
passé antérieur à celui que l'on
évoquait
(V-ing): Insistance sur le
déroulement ou la durée de
l'action
I saw the end before we’d begun..
I saw you were blinded and I knew I had
won. (James Blunt, Goodbye my lover)
S= sujet BV= base verbale V-ing= verbe à la forme –ing p .p= participe passé
* l’emploi de l’auxiliaire + radical verbal à l’affirmatif est une forme d’insistance ex : I did go to Spain. Je suis vraiment allé en Espagne.
Toujours
une
proposition
au prétérit
pour servir
de repère
temporel
1
/
2
100%