Management information system A management information system

Management information system
A management information system (MIS) is a subset of the overall internal controls of a business
covering the application of people, documents, technologies, and procedures by management
accountants to solve business problems such as costing a product, service or a business-wide
strategy. Management information systems are distinct from regular information systems in that
they are used to analyze other information systems applied in operational activities in the
organization.[1] Academically, the term is commonly used to refer to the group of information
management methods tied to the automation or support of human decision making, e.g. Decision
Support Systems, Expert systems, and Executive information systems.[1]
It has been described as, "MIS 'lives' in the space that intersects technology and business. MIS
combines tech with business to get people the information they need to do their jobs
better/faster/smarter. Information is the lifeblood of all organizations - now more than ever. MIS
professionals work as systems analysts, project managers, systems administrators, etc.,
communicating directly with staff and management across the organization." [2]Contents [hide]
Overview
At the start, in businesses and other organizations, internal reporting was made manually and only
periodically, as a by-product of the accounting system and with some additional statistics, and gave
limited and delayed information on management performance.
In their infancy, business computers were used for the practical business of computing the payroll
and keeping track of accounts payable and accounts receivable. As applications were developed that
provided managers with information about sales, inventories, and other data that would help in
managing the enterprise, the term "MIS" arose to describe these kinds of applications. Today, the
term is used broadly in a number of contexts and includes (but is not limited to): decision support
systems, resource and people management applications, project management and database
retrieval application.
Definition
An 'MIS' is a planned system of the collecting, processing, storing and disseminating data in the form
of information needed to carry out the functions of management. In a way it is a documented report
of the activities those were planned and executed. According to Philip Kotler "A marketing
information system consists of people, equipment, and procedures to gather, sort, analyze,
evaluate, and distribute needed, timely, and accurate information to marketing decision makers." [3]
The terms MIS and information system are often confused. Information systems include systems
that are not intended for decision making. The area of study called MIS is sometimes referred to, in a
restrictive sense, as information technology management. That area of study should not be confused
with computer science. IT service management is a practitioner-focused discipline. MIS has also
some differences with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) as ERP incorporates elements that are not
necessarily focused on decision support.
Professor Allen S. Lee states that "...research in the information systems field examines more than
the technological system, or just the social system, or even the two side by side; in addition, it
investigates the phenomena that emerge when the two interact." [4].
Système d'information de gestion

Un système d'information de gestion (SIG)(aussi système intégré de gestion, GSI ou encore système
de pilotage) repose sur la mise en place d'indicateurs permettant de suivre en permanence les
principaux résultats des divers secteurs d'activité d'une entreprise (secteur commercial, production,
finance, ressources humaines, etc.) par rapport aux prévisions, objectifs et budgets.
Il aide aussi à la prise de décision, tant au niveau stratégique qu'au niveau opérationnel courant.
Il est également de plus en plus utilisé par d'autres institutions que les entreprises commerciales
(administrations, associations...)
Le système sert tant à la direction générale qu'à chaque unité de l'organisme, par exemple dans une
optique de Direction par objectifs.
Un tel système fait largement appel à l'utilisation d'une base de données de gestion traitée par
informatique

Système d'information de gestion des ressources humaines
Aller à : Navigation, rechercher
Un Système d'information de gestion des ressources humaines (en : Human Resource Management
Systems (HRMS, EHRMS), Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS), HR Technology ou encore
HR modules), est une interface entre la gestion des ressources humaines (GRH) et les technologies
de l'information et de la communication (TIC). Il combine la GRH, et en particulier ses activités
basiques et administratives (payroll, gestion administrative), avec les moyens mis à disposition par
les TIC. Sont notamment concernées les activités de planning et de traitement de données
généralement destinées à être intégrée dans un progiciel de gestion intégré ( en : Enterprise
Resource Planning ou ERP). Les systèmes ERP sont des programmes informatiques intégrant les
informations issues de différentes origines dans une entreprise en des modules intégrés dans une
seule application et une base de données unique. La qualité de la liaison entre les modules financiers
et de ressources humaines est particulièrement importante pour les entreprises, étant donné le
poids financier généralement très important des ressources humaines.
Les TIC proposent également d'importants développements pour la GRH autres que pour la gestion
interne et intégrée à la gestion financière d'une entreprise, telles les applications développées en
intra- ou extranet concernant le recrutement et l'E-learning. Elle permettrent également une
externalisation simplifiée des tâches susceptibles d'être informatisées, et des relations électroniques
directes avec les administrations (E-Gouvernement).Sommaire [masquer]
1 Implémentation des Systèmes d'information de GRH dans une organisation
2 Acteurs sur le marché des Systèmes d'information en GRH
3 Le Cercle SIRH
4 Voir aussi
4.1 Articles connexes
5 Notes et références
Implémentation des Systèmes d'information de GRH dans une organisation [modifier]
Dans l'ensemble, la fonction "ressources humaines" comprend toujours une part importante de
tâches administratives et répétitives dans la plupart des organisations. La plupart de celles-ci sont à
un niveau plus ou moins important intégré les opérations d'établissement et de paiement des
rémunérations, de présence des travailleurs, des évaluations ou encore du recrutement et des
évolutions de carrière.
Une gestion efficace du "capital humain" est devenue une opération nécessaire et complexe pour les
professionnels des ressources humaines. Leur fonction consiste en premier à collecter des données
pour chaque travailleur, concernant son histoire et caractéristiques personnelles, ses compétences
et capacités, jusqu'à des données plus accessibles telles ses rémunérations et ses prestations
effectuées pour l'entreprise. La quantification de ces données et la systématisation de leur
traitement complexe a permis leur prise en charge par des systèmes automatisés au fur-et-à-mesure

de la progression technologique, en réduisant d'autant la part manuelle des opérations, coûteuse et
source d'erreurs.
Ceux-ci ont conduit à la mise en place des systèmes d'information appliqués à la gestion des
ressources humaines, et dans certains cas à l'externalisation de ces activités. La maîtrise de ces outils
est désormais largement déléguée aux spécialistes TIC internes ou externes à l'organisation. Avant
l'apparition de l'architecture "client-serveur" qui s'est développée fin des années 1980, les
applications informatiques dédiées aux ressources humaines accédaient directement aux
ordinateurs mainframes et leur capacité de traitement rapide. Du fait du coût et de la spécialisation
/ personnalisation de ces applications, leur acquisition était limitée à des organisations d'une
certaine taille, capable de mobiliser les ressources informatiques internes ou externes suffisantes.
Avec l'arrivée des applications sous architecture client-serveur, les systèmes d'information de GRH
permirent pour la première fois aux responsables RH de retrouver une maîtrise des opérations de
gestion administrative, les professionnels TIC étant cantonnés aux aspects purement techniques. Ces
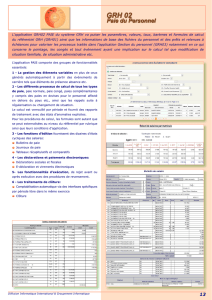
systèmes d'information de GRH sous architecture client-serveur sont construits autour de quatre
domaines RH spécifiques :
gestion de la paie
gestion des prestations de travail
gestion des prestations sociales
gestion des ressources humaines proprement dites (carrières, compétences, recrutement…)
1. Le module de paie automatise la gestion de la paie en rassemblant les données mise à disposition
pour le travailleur concernant ses prestations et leur nature, y applique les déductions, préléve la
cotisation sociale et génère périodiquement un compte individuel et une proposition d'ordre de
versement de la rémunération. Il permet également de générer des données et statistiques pour
l'ensemble du personnel concernant ces données. Les données des prestations peuvent être
générées automatiquement (pointeuses) ou via un encodage. Les informations peuvent par ailleurs
être envoyées vers un module financier.
2. Le module de gestion des prestations de travail permet d'intégrer les TIC et des méthodes
rationnelles pour la gestion des prestations de travail. Les modules les plus avancés intègrent les
politiques de flexibilité pour l'analyse des données, et des analyses et des propositions de planning
dans la répartition du travail. Cette partie de l'application est à mettre en étroit parallèle avec des
éléments de gestion financière et de production.
3. Le module de gestion des prestations sociales permet aux professionnels RH de gérer au mieux les
prestations sociales obligatoires ou non, tels l'assurance maladie, l'assurance accidents de travail, les
assurances-pension complémentaires.
4. Le module de gestion des ressources humaines concerne les autres aspects des RH, comprenant
moins de contraintes légales mais plus sujet à une politique de gestion. La gestion de la carrière du
travailleur, de son recrutement jusqu'à la pension, y est en particulier développée. Sont ici gérées les
données personnelles (âge, adresse, famille…), les compétences et diplômes, les formations suivies,
les niveaux de salaire et la fonction, l'enregistrement des données du curriculum vitæ.

Le Système d'information de GRH permet d'intégrer ces quatre segments de la GRH en créant des
liaisons fonctionnelles entre ces activités au sein du logiciel.
L'internet peut être utilisé comme moyen de communication et d'envoi de fichiers, et les systèmes
d'information de GRH permettent de convertir ces données vers une interface de type navigateur
Internet utilisée par l'ERP. Ce type d'interface avec le système permet une portabilité et un moindre
coût pour l'accès aux systèmes de gestion, augmentant ainsi l'efficience de la GRH. Les travailleurs
ou les responsables de services peuvent aussi avoir un accès partiel au système, qui leur permet par
exemple d'entrer eux-mêmes les données le concernant, tel une demande de congé.
Ces tâches coûteuses en temps et en argent, telles la gestion administrative du personnel ou le
remboursement de déplacements, le changement des données personnelles, l'inscription à une
formation à un plan de pension peuvent dès lors être effectuées par la personne qui est directement
à l'origine de l'action à réaliser. Ces systèmes libèrent ainsi le personnel de RH de tâches fastidieuses
et répétitives, leur permettant de se concentrer sur des problèmes plus décisionnels, stratégiques ou
politiques et economiques
Acteurs sur le marché des Systèmes d'information en GRH [modifier]
Les principales entreprises proposant des ERP pour la gestion des ressources humaines sont : ADP,
Cegid RH, ADEQUASYS, SAP HR, SIGMA-RH, Oracle, HR Access, meta4, Lawson, CEGEDIM SRH, SAGE,
Cezanne Sofware, Technomedia, TEHMS, Jobpartners, SAGES Software, EXTALYS.
De très nombreuses autres entreprises proposent des programmes pour des applications
particulières telles que la gestion des présences des travailleurs, éventuellement directement liée au
système de payroll.
Il existe également des sociétés de conseil qui collaborent à la conception et la mise en œuvre des
SIRH.
Des acteurs en conseil en SIRH accompagnent les entreprises dans leurs projets SIRH, lancement
d'appel d'offre, conception, audit, pilotage de projet mais aussi formation métier. D'autres acteurs
se spécialisent dans des sous-ensembles des SIRH comme par exemple la gestion des recrutements.
La tendance depuis 2003 est de se concentrer vers des solutions en mode ASP (application service
providing), certaines entreprises proposent un service en ligne d'évaluation des formations ou de
gestion du recrutement. On parle alors de Software as a service.
Le Cercle SIRH [modifier]
Le Cercle SIRH regroupe des responsables SIRH de grandes entreprises françaises autour de
problématiques communes à leur métier. Son fonctionnement repose sur l’organisation de journées
d’études thématiques chaque trimestre. Il est indépendant de tout éditeur de solutions progicielles
et de tout club utilisateurs. Les participants ont des outils qui reflètent la diversité du marché. Les
responsables SIRH peuvent ainsi comparer les solutions retenues et contribuer à la diffusion de
bonnes pratiques au sein de leur profession. Il met à la disposition de ses membres et du public
intéressé son blog1.
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
1
/
16
100%