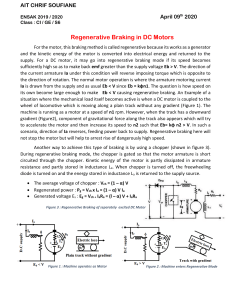
A Conventional DC Machines and Universal Motor 45
When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to demonstrate the
main operating characteristics of a separately-excited dc motor using the
DC Motor/Generator.
Simplified equivalent circuit of a dc motor
Previously, you saw that a dc motor is made up of a fixed magnet (stator) and a
rotating magnet (rotor). Many dc motors use an electromagnet at the stator, as
Figure 2-8 shows.
Figure 2-8. Simplified dc motor using an electromagnet as stator.
When power for the stator electromagnet is supplied by a separate dc source, of
either fixed or variable voltage, the motor is known as a separately-excited
dc motor. Sometimes the term independent-field dc motor is also used. The
current flowing in the stator electromagnet is often called field current because it
is used to create a fixed magnetic field.
TheSeparately‐ExcitedDCMotor
Exercise2‐1
EXERCISE OBJECTIVE
DISCUSSION
Stator
(electromagnet)
NS
Rotor
(armature)

Ex. 2-1 – The Separately-Excited DC Motor Discussion
46 Conventional DC Machines and Universal Motor A
The electrical and mechanical behavior of the dc motor can be understood by
examining its simplified equivalent electric circuit shown in Figure 2-9.
Figure 2-9. Simplified equivalent circuit of a dc motor.
In the circuit, is the voltage applied to the motor brushes, is the current
flowing in the armature through the brushes, and is the resistance between
the brushes. Note that , , and are usually referred to as the armature
voltage, current, and resistance, respectively. is the voltage drop across the
armature resistor. When the motor turns, an induced voltage proportional
to the speed of the motor is produced. This induced voltage is represented by a
dc source in the simplified equivalent circuit of Figure 2-9. The motor also
develops a torque
T
proportional to the armature current flowing in the motor.
The motor behavior is based on the two equations given below. Equation (2-1)
relates motor speed
n
and the induced voltage . Equation (2-2) relates the
motor torque
T
and the armature current .
K
(2-1)
where is the motor rotation speed, expressed in revolutions per
minute (r/min).
K
is a constant expressed in /
.
is the voltage induced across the armature, expressed in
volts (V).
K
(2-2)
where is the motor torque, expressed in newton-meters (N·m) or in
pound-force inches (lbf∙in).
K
is a constant expressed in ∙
or
∙
.
is the armature current, expressed in amperes (A).
+
+

Ex. 2-1 – The Separately-Excited DC Motor Discussion
A Conventional DC Machines and Universal Motor 47
Relationship between the motor rotation speed and the armature
voltage
When a voltage is applied to the armature of a dc motor with no mechanical
load, the armature current flowing in the equivalent circuit of Figure 2-9 is
constant and has a very low value. As a result, the voltage drop across the
armature resistor is so low that it can be neglected, and can be considered
to be equal to the armature voltage . Therefore, the relationship between the
motor rotation speed
n
and the armature voltage is a straight line
because is proportional to the motor rotation speed
n
. This linear
relationship is shown in Figure 2-10. The slope of the straight line equals
constant K.
Figure 2-10. Linear relationship between the motor rotation speed and the armature voltage.
Since the relationship between voltage and the rotation speed
n
is linear, a
dc motor can be considered to be a linear voltage-to-speed converter, as shown
in Figure 2-11.
Figure 2-11. DC motor as a voltage-to-speed converter.
Motor speed
n
(r/min)
Armature voltage
(V)
Slope K
Output motor rotation speed
n
Input armature voltage K1

Ex. 2-1 – The Separately-Excited DC Motor Discussion
48 Conventional DC Machines and Universal Motor A
Relationship between the motor torque and the armature current
The same type of relationship exists between the motor torque
T
and the
armature current , so that a dc motor can also be considered as a linear
current-to-torque converter. Figure 2-12 illustrates the linear relationship between
the motor torque
T
and the armature current . Constant K is the slope of the
line relating the two. The linear current-to-torque converter is shown in
Figure 2-13.
Figure 2-12. Linear relationship between the motor torque and the armature current.
Figure 2-13. DC motor as a current-to-torque converter.
Motor torque
T
(N·m or lbf·in)
Armature current
(A)
Slope K
Output motor torque
T
Input armature current

Ex. 2-1 – The Separately-Excited DC Motor Discussion
A Conventional DC Machines and Universal Motor 49
Relationship between the motor rotation speed and the armature
voltage
When the armature current increases, the voltage drop (
) across the
armature resistor also increases and can no longer be neglected. As a result, the
armature voltage can no longer be considered equal to , but rather the
sum of and , as Equation (2-3) shows:
(2-3)
Therefore, when a fixed armature voltage is applied to a dc motor, the voltage
drop across the armature resistor increases as the armature current
increases, and thereby, causes to decrease. This also causes the motor
rotation speed
n
to decrease because it is proportional to . This is shown in
Figure 2-14, which is a graph of the motor rotation speed
n
versus the armature
current for a fixed armature voltage .
Figure 2-14. The motor rotation speed drops as the armature current increases (fixed armature
voltage ).
Armature current (A)
Fixed armature voltage
Motor speed
n
(r/min)
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
1
/
15
100%