Photovoltaics – Exercise 1
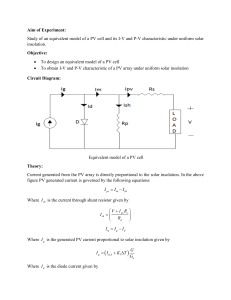
solar cell principles
The bandgap of GaAs is 1,52 eV at 0K and 1,42 eV at 300K.
a) Calculate the cutoff wavelength at each temperature.
, =
, =
b) The internal quantum efficiency of the cell is 96% at 600nm and 89% at
800nm. The following also applies: R = 5% (600nm) and R = 3% (800nm).
Calculate the external quantum efficiency assuming T = 0 (λ <cut-off
wavelength) for both wavelengths.
()=,%
()=,%
c) Calculate the spectral sensitivity at 600, 800 and 900nm
()=,
(
)
=,
⇒ ()=
>
d) Consider an ideal GaAs solar cell. Calculate the open circuit voltage under the
following assumptions: Photo current density: 26mA/cm² and reverse
saturation current density Js,GaAs= 2*10-16 mA/cm², the temperature voltage
VT = 25,9mV at 300K.
=,
e) What is the efficiency of the GaAs solar cell (assumption: FF=82%)
=,%
f) Calculate the diffusion voltage of the GaAs solar cell at room temperature. The
following charge carrier densities can be assumed:
ni,GaAs=1,8*106 cm-3, nD,GaAs = 5*1015 cm-3, nA,GaAs = 5*1017 cm-3
=,
g) Calculate the minority carrier densities in the p- and the n-regions.

=, ∙−
=, ∙−

Photovoltaics – Exercise 2
Current, voltage, efficiency
We consider an amorphous silicon solar cell with the following properties:
STC
60 °C und 850 W/m²
open circuit voltage
V
OC
0,9 V
0,86 V
MPP-voltage
V
MPP
0,7 V
0,65 V
Short circuit current density
J
SC
12,3 mA/cm²
10,6 mA/cm²
fill factor
FF
63%
61%
The irradiance correction factor for the open circuit voltage is 0.03.
a) Calculate the current density at the MPP:
• under STC
• at 60° C cell temperature and 850W / m² irradiation
, =,
; ,° /²=,
b) Calculate the temperature coefficients for VOC and VMPP
=, ; =,
c) Calculate the temperature coefficients for ISC und IMPP.
=, ; =,
d) How much does the efficiency decrease under the above conditions compared to
STC conditions?
=,% ; °
=,% =,%
e) The cell is to be used as radiation sensor. A short-circuit current density of 7.8 mA /
cm² is measured at 40 °C cell temperature. Calculate the irradiance.
Assumption: ,°=,°=,
=
²

Photovoltaics - Exercise 3
grid connected PV-system
Dimension a grid connected PV-system on a southeast roof with a dimension of 5 x 8 m²
with 35° inclination in Cologne with the goal of reaching minimum cable cross-sections.
You should use 16 solar modules with 375 W nominal output power as given below.
Select one of the inverters shown in the annex (table 2).
a) Dimension the inverter by considering the nominal power range, the MPP-voltage
range und the maximum input voltage of the inverter at the following operating
conditions: -10°C, 70°C and 1000W/m² irradiation.
Choose a suitable inverter from table 2. One string shall be used, if possible.
⇒ inv4
b) Calculate the cross section of the cable with 50m length (one-way!) to the inverter.
Electric conductivity κCu =56m/(Ω*mm²), common cross-sections: 2,5mm², 4mm²,
6mm², 10mm² oder 25mm².
⇒ =²
Module data sheet
Rated power at MPP
P
mpp
375
Wp
Module efficiency
η
21,4
%
Nominal voltage at MPP
V
mpp
38,7
V
Nominal current at MPP
I
mpp
9,71
A
Open circuit voltage
V
oc
45,2
V
Short circuit current
I
sc
10,23
A
Maximum reverse current
I
R
25,00
A
Maximum system voltage
1000,00
V
Temperature coeeficient of Vmpp and
Voc
β
-0,24
% /° C
Dimensions
1,72 m x 1 m
inverter data-sheet
inv1 inv2 inv3 inv4 inv5
Max. DC-power [W]
4.000 5.500 6.200 6.000 7.100
Max. input current [A]
16,5 9,2 14 17,4 18
Max. input voltage [A]
800 800 800 850 740
MPP-voltage range [V]
200-700 200-700 200-600 350-750 300-750
MPP-voltage range [V]
1 1 1 1 1

Photovoltaics – Exercise 4
power supply grid
A single-phase grid-controlled inverter with a pulse number of 12 and cosϕ = 1 has an AC
nominal power of 3.8 kW and a nominal voltage of 230 V. There is no information regarding
harmonics. We consider the following connection point (AP) on land (overhead line):
nominal transformer power
P
nenn
100
kVA
Reactance coating
X‘
L
0,33
mΩ/m
Specific resistance of copper
ρ
0,02
Ωmm²/m
single cable length
l
130
m
Cable cross section
A
75
mm²
a) Calculate the resistance and reactance of the lines.
=,
=,
b) Determine the resistance and reactance of the transformer (see lecture 5).
=,
=
c) Calculate the line impedance.
=,
d) Calculate the short-circuit power at the AP.
=,
e) Form the quotient of the short-circuit power at the AP and the nominal inverter
power. What conclusion can be drawn from this finding?
=,
f) Determine the permissible connection power with max. 3% increase in voltage.
=,
g) Can the WR be connected? Discuss the result!
yes
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
1
/
13
100%