Contents
Advanced Cardiac Life Support ................................. 5
Critical Care Patient Management .............................. 15
Critical Care History and Physical Examination ................... 15
Critical Care Physical Examination ............................. 15
Admission Check List ....................................... 16
Critical Care Progress Note .................................. 17
Procedure Note ............................................ 17
Discharge Note ............................................ 18
Fluids and Electrolytes ...................................... 18
Blood Component Therapy ................................... 18
Total Parenteral Nutrition .................................... 19
Enteral Nutrition ........................................... 20
Radiographic Evaluation of Interventions ........................ 20
Arterial Line Placement ...................................... 21
Central Venous Catheterization ............................... 21
Normal Pulmonary Artery Catheter Values ....................... 24
Cardiovascular Disorders ..................................... 25
Acute Coronary Syndromes .................................. 25
Myocardial Infarction and Unstable Angina ....................... 25
Heart Failure .............................................. 32
Atrial Fibrillation............................................ 36
Hypertensive Emergency .................................... 41
Ventricular Arrhythmias ...................................... 44
Torsades de Pointes ........................................ 44
Acute Pericarditis .......................................... 45
Pacemakers .............................................. 46
Pulmonary Disorders ......................................... 49
Orotracheal Intubation ....................................... 49
Nasotracheal Intubation ..................................... 50
Ventilator Management ...................................... 51
Inverse Ratio Ventilation ..................................... 52
Ventilator Weaning ......................................... 52
Pulmonary Embolism ....................................... 54
Asthma .................................................. 58
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease ........................ 62
Pleural Effusion ............................................ 65
Trauma .................................................... 67
Pneumothorax ............................................. 67
Tension Pneumothorax ...................................... 68
Cardiac Tamponade ........................................ 69
Pericardiocentesis .......................................... 69
Hematologic Disorders ....................................... 71
Transfusion Reactions ...................................... 71
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation ......................... 72
Thrombolytic-associated Bleeding ............................. 73

Infectious Diseases .......................................... 75
Bacterial Meningitis ......................................... 75
Pneumonia ............................................... 79
Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia .............................. 83
Antiretroviral Therapy and Opportunistic Infections in AIDS .......... 85
Sepsis ................................................... 87
Peritonitis ................................................ 91
Gastroenterology ............................................ 93
Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding ............................... 93
Variceal Bleeding .......................................... 94
Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding ............................... 96
Acute Pancreatitis .......................................... 99
Hepatic Encephalopathy .................................... 102
Toxicology ................................................. 105
Poisoning and Drug Overdose ............................... 105
Toxicologic Syndromes ..................................... 106
Acetaminophen Overdose ................................... 106
Cocaine Overdose ........................................ 108
Cyclic Antidepressant Overdose .............................. 109
Digoxin Overdose ......................................... 109
Ethylene Glycol Ingestion ................................... 110
Gamma-hydroxybutyrate Ingestion ............................ 111
Iron Overdose ............................................ 111
Isopropyl Alcohol Ingestion .................................. 112
Lithium Overdose ......................................... 112
Methanol Ingestion ........................................ 113
Salicylate Overdose ....................................... 113
Theophylline Toxicity ....................................... 114
Warfarin (Coumadin) Overdose .............................. 115
Neurologic Disorders ........................................ 117
Ischemic Stroke ........................................... 117
Elevated Intracranial Pressure ............................... 120
Status Epilepticus ......................................... 122
Endocrinologic and Nephrologic Disorders ..................... 125
Diabetic Ketoacidosis ...................................... 125
Acute Renal Failure ........................................ 127
Hyperkalemia ............................................ 130
Hypokalemia ............................................. 133
Hypomagnesemia ......................................... 134
Hypermagnesemia ........................................ 135
Disorders of Water and Sodium Balance ....................... 136
Hypophosphatemia ........................................ 140
Hyperphosphatemia ....................................... 141
Commonly Used Formulas ................................... 142
Commonly Used Drug Levels ................................. 142
Index ..................................................... 144

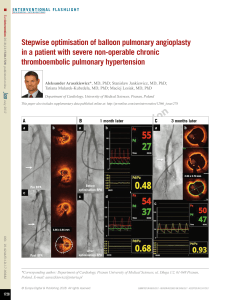
Advanced Cardiac Life Support
EMERGENCY CARDIAC CARE
If wi tnessed arrest, give
precord ial thump and
check pulse. If absent,
continue CP R
Assess Re spo nsiveness
Unresponsive
Call for code team and De fibr illato r
Assess breathing (op en the airway, look,
liste n an d feel for breathing)
If Not Bre ath ing,
give two slow b reaths.
Assess Cir cula tion
PULSE NO PULSE
Initia te CPR
Give oxygen by bag mask
Secure IV access
Dete rmine proba ble e tiol ogy of arrest
based on histo ry, physical exam, car diac
monitor, vital signs, and 12 lead ECG.
Ven tricular
fibrillation/tach ycardia
(VT/VF) p rese nt on
monitor?
Hypo ten sion /shock,
acute p ulmonary
edema .
Go to fig 8 NO YES
Intu bate
Confirm tube pla ceme nt
Dete rmine rhythm and
cause.
VT/VF
Go to Fig 2
Arrh ythmia
Brad ycardia
Go to Fig 5 Tachycardia
Go to Fig 6 Electrical A ctivity?
YES NO
Pulseless e lectrical activity
Go to Fig 3 Asystole
Go to Fig 4
Fig 1 - Algorithm for Adult Emergency Cardiac Care

VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION AND PULSELESS
VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA
Con tinue CPR
Persist ent or
recurrent V F/VT
Epinep hrine 1 mg
IV pu sh, re pe at
q3 -5min o r 2 m g in
10 ml NS via ET t ube
q3 -5min or
Vasopressin 40 U I VP x
1 do se o nly
Def ibrillate 360 J
Amiodarone (Cordarone) 300 mg IV P or
Lido ca in e 1. 5 mg /k g IV P, an d repe a t q 3-5 min, u p t o to ta l max o f 3 mg/ kg or
Magnesium s ulf at e (if Tors ade de poin te s or hypo ma gn es emic ) 2 gms IV P or
Procaina mide (if ab ove are in ef fec tive ) 3 0 mg/min I V inf u sion to ma x 17 mg/kg
Continue CPR
Secure IV access
In tubat e if no respo nse
Def ib rillate immediately, u p to 3 times at 20 0 J, 20 0-30 0 J, 36 0 J.
Do not de la y defibrillation
Return of
spo nt ane ou s
circulation
Pu lseless E lectrical
Act ivity
Go to Fig 3
Monit or vital sign s
Su pp or t a irway
Su pp or t b re athing
Provide me dications appropriate fo r bloo d
pre ssure, hea rt rate, and rhythm
Asse ss Airway, Bre ath ing, Circulation, Diffe rent ial Diagnosis
Ad min ister CPR u ntil d efibrillato r is ready (p recordia l thu mp if witn esse d arrest )
Ve ntricular Fibrillation or Ta chycardia presen t on defibrillator
Asyst ole
Go to Fig 4
Check pu lse and Rhythm
Co nt inue CP R
De fibrilla te 36 0 J, 30- 60 seconds af te r ea ch dose of me dication
Repe at amio daro ne (Cord arone ) 15 0 mg IV P prn (if re urrent VF/ VT) , up to ma x
cu mulative do se of 22 00 mg in 24 ho urs
Cont in ue CP R. Ad minist er s odium bicarbonate 1 mEq/k g I VP if long arres t period
Repe at patt ern o f d rug -sho ck, drug-sho ck
Note: Epinephrine, lidocaine, atropine may be given via endotracheal tube at
2-2.5 times the IV dose. Dilute in 10 cc of saline.
After eac h in travenous dos e, give 20 -30 mL bolus of IV f luid and elev at e
extremity.
Fig 2 - Ventricular Fibrillation and Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia

PULSELESSELECTRICALACTIVITY
PulselessElectrical Activity Includes:
Electromechanical dissociation (EMD)
Pseudo-EMD
Idioventricularrhythms
Ventricular escaperhythms
Bradyasystolic rhythms
Postdefibrillation idioventricularrhythms
Epinephrine 1.0 mgIVbolus q3-5min, or high dose
epinephrine0.1 mg/kg IVpushq3-5min; maygivevia
ETtube.
ContinueCPR
If bradycardia (<60beats/min), giveatroprine 1 mgIV, q3-5
min, upto total of 0.04mg/kg
Consider bicarbonate, 1mEq/kg IV(1-2amp, 44 mEq/amp),
if hyperkalemiaor other indications.
Determine differential diagnosis and treat underlying cause:
Hypoxia (ventilate)
Hypovolemia (infuse volume)
Pericardial tamponade (performpericardiocentesis)
Tension pneumothorax (performneedle decompression)
Pulmonary embolism (thrombectomy, thrombolytics)
Drug overdose with tricyclics, digoxin, beta, or calciumblockers
Hyperkalemia or hypokalemia
Acidosis (give bicarbonate)
Myocardial infarction (thrombolytics)
Hypothemia(active rewarming)
Initiate CPR, secure IV access, intubate, assess pulse.
Fig 3 - Pulseless Electrical Activity
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
 45
45
 46
46
 47
47
 48
48
 49
49
 50
50
 51
51
 52
52
 53
53
 54
54
 55
55
 56
56
 57
57
 58
58
 59
59
 60
60
 61
61
 62
62
 63
63
 64
64
 65
65
 66
66
 67
67
 68
68
 69
69
 70
70
 71
71
 72
72
 73
73
 74
74
 75
75
 76
76
 77
77
 78
78
 79
79
 80
80
 81
81
 82
82
 83
83
 84
84
 85
85
 86
86
 87
87
 88
88
 89
89
 90
90
 91
91
 92
92
 93
93
 94
94
 95
95
 96
96
 97
97
 98
98
 99
99
 100
100
 101
101
 102
102
 103
103
 104
104
 105
105
 106
106
 107
107
 108
108
 109
109
 110
110
 111
111
 112
112
 113
113
 114
114
 115
115
 116
116
 117
117
 118
118
 119
119
 120
120
 121
121
 122
122
 123
123
 124
124
 125
125
 126
126
 127
127
 128
128
 129
129
 130
130
 131
131
 132
132
 133
133
 134
134
 135
135
 136
136
 137
137
 138
138
 139
139
 140
140
 141
141
 142
142
 143
143
 144
144
 145
145
 146
146
 147
147
 148
148
 149
149
 150
150
1
/
150
100%