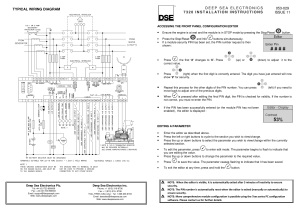
Global Maintenance Management

Maintenance Objectives
•Maximize Production.
•Minimize Energy Consumption.
•Reduce Breakdowns.
•Reduce Downtime.
•Improve Equipment Efficiency & Life Time.
•Control Annual Budget.
•Optimize Resources Utilization.
•Minimize Total Cost / Ton.
•Increase Product Quality.
•Improve Safety Level.

CONTENTS:
Finally: Why should I have to know this level of managerial knowledge NOW ???
•Key of Performance Indicators.
•Reliability and Availability.
•Maintenance Strategy.
•Maintenance Cost.

Maintenance Strategy

Maintenance
Policies
Unplanned
Stoppage
Planned
Stoppage
Failure BaseRisk Base
Condition
Base
Time Base
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
1
/
23
100%