Periodontitis: What Are The
Different Stages?
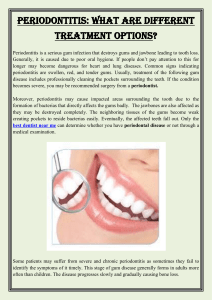
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory gum disease caused by a bacterial infection
surrounding the gum tissues. The disease can affect anyone and is very common in people
over the age of thirty-five. The disease is caused by the inflammation and infection of the
gums. And if it is left untreated for a longer period, you may have bone loss surrounding the
teeth. You can notice the signs in the early stage of adolescence but its progressive nature is
often diagnosed in the fourth to fifth decade of life. You can know more about it through
Delta Dental Ppo Dentists.
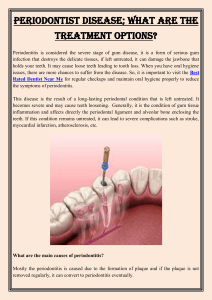
With passing time, without the Gum Disease Treatment, the infection starts to spoil the
jawbone that holds the teeth. The damage weakens the connected tissues and loosens the
teeth that may fall eventually.
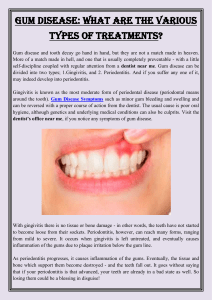
When the deep sacs of teeth are filled with plaque and pus, starts feeling foul taste in the
mouth resulting in difficulty in teeth cleaning at home. With the progression of the disease,
the root surfaces which become exposed are very sensitive to hot and cold things. Since the
exposed root surface does not have a protective root enamel, are more likely to develop
cavities. You can get the treatment at the dental office.
Types of Periodontitis:
There are five types of periodontitis:

1) Chronic Periodontitis -
This stage of gum disease includes periodontal pockets that slowly and gradually develop. It
can be additionally classified into localized or generalized versions like mild, moderate, or
severe.
2) Aggressive Periodontitis -
The stage involves failure of periodontal attachment at a brisk pace related to the patients’
age. In addition, it can be divided into localized or generalized forms, as well as the mild,
moderate, or severe amount of injury. Often, it can be noticed in adulthood and may transfer
in families. People who are suffering from the following issues may experience defects in
their immune systems.
3) Periodontitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Disease:
Patients suffering from leukemia (a blood disease) or Down syndrome (genetic diseases) are
more likely to have periodontitis. Mainly, it is due to the inability to fight infection.
4) Necrotizing Ulcerative Periodontitis (NUP):
This stage is connected with the severity of pain and bone loss. The patient may also
experience gum ulcers and bad breath. The main contributing factors involve Malnutrition,
psychological stress, smoking, lack of sleep, and incapacity to fight infections. NUP was also

referred to as trench mouth after the detection of its symptoms in soldiers returning from the
trenches of World War I.
5) Periodontitis Associated with Endodontic Lesions:
This form of the disease can affect the patient who has an infected tooth requiring a root
canal or endodontic therapy, in this case, there may be a bone loss at the tip of the root.
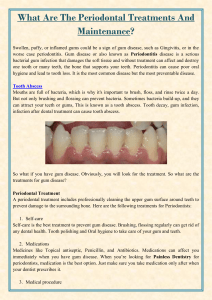
Periodontitis Treatment:
Unlike gingivitis treatment, which usually can be eliminated by good oral hygiene and
professional cleaning, periodontitis may require repeat visits to the dentist. The regular
hygiene practice i.e Brushing and flossing only clean 1-3 millimeters below the gum line and
periodontal pockets of up to 4-10 millimeters. Therefore, when deep pockets are present,
deeper cleaning is necessary. Such a type of treatment is called scaling and root planning that
helps to remove complete plaque and calculus below the gumline and primes the root for
reattachment of the gums. It is similar to regular cleaning, but is more meticulous and goes
further below the gumline. For this reason, a Good Dentist Near Me may administer a local
anesthetic to numb the gums.
1
/
3
100%