S P E A K E R :
D R . MD. S H A I F U L H A S S A N S H A M E E M
A S S I S T A N T R E G I S T R A R
D E P T . O F R A D I O T H E R A P Y
D H A K A M E D I C A L C O L L E G E H O S P I T A L
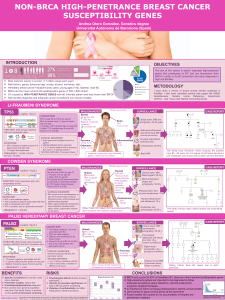
INTRODUCTION
TO
CANCER GENETICS

The genetic nature of Cancer
Cancer is a complex disease that result from the basic
process of uncontrolled growth. Cell proliferation results in
a mass that invades neighboring tissues and may
metastasize to more distant sites.
In order for a normal cell to transform into a cancer
cell, genes which regulate cell growth and
differentiation must be altered. When normal regulation
is altered, uncontrolled growth is initiated and a malignant
tumor develop.
Genetic changes can occur at many levels, from gain or
loss of entire chromosomes to a mutation affecting a single
DNA nucleotide.

Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis is a multistep
process at both the phenotypic &
genetic levels, resulting from the
accumulation of multiple mutation.

A tumor is formed by the
clonal expansion of a
precursor cell that has
incured genetic damage.
Even though most
malignant tumors are
monoclonal in origin, by the
time they become clinically
evident their constituent
cells are heterogenous.

Cancer arises from the accumulation of genetic aberrations
in somatic cells
These aberrations consist of mutations and chromosome
defects
Epigenetic aberrations are also present
Together, they lead to altered gene expression
Over 500 genes are now known to be involved in cancer
development
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
1
/
38
100%


![[PDF]](http://s1.studylibfr.com/store/data/008642620_1-fb1e001169026d88c242b9b72a76c393-300x300.png)