TFG ivettefernandezrodriguez
publicité
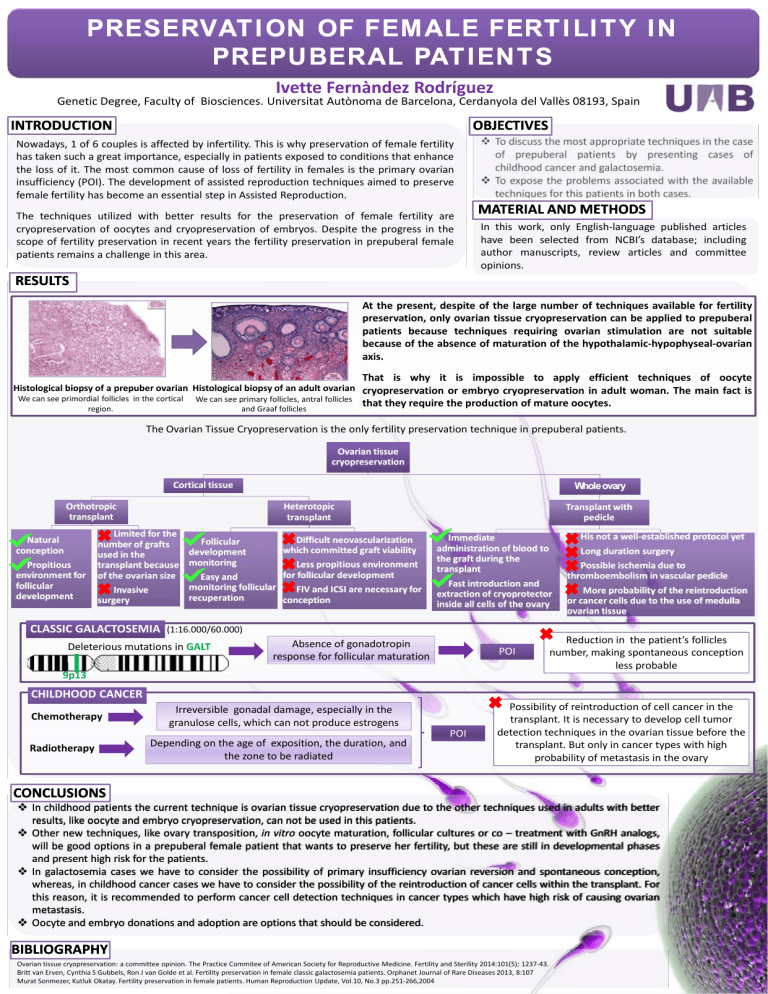
PRESERVATION OF FEMALE FERTILITY IN PREPUBERAL PATIENTS Ivette Fernàndez Rodríguez Genetic Degree, Faculty of Biosciences. Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Cerdanyola del Vallès 08193, Spain INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES Nowadays, 1 of 6 couples is affected by infertility. This is why preservation of female fertility has taken such a great importance, especially in patients exposed to conditions that enhance the loss of it. The most common cause of loss of fertility in females is the primary ovarian insufficiency (POI). The development of assisted reproduction techniques aimed to preserve female fertility has become an essential step in Assisted Reproduction. The techniques utilized with better results for the preservation of female fertility are cryopreservation of oocytes and cryopreservation of embryos. Despite the progress in the scope of fertility preservation in recent years the fertility preservation in prepuberal female patients remains a challenge in this area. To discuss the most appropriate techniques in the case of prepuberal patients by presenting cases of childhood cancer and galactosemia. To expose the problems associated with the available techniques for this patients in both cases. MATERIAL AND METHODS In this work, only English-language published articles have been selected from NCBI’s database; including author manuscripts, review articles and committee opinions. RESULTS At the present, despite of the large number of techniques available for fertility preservation, only ovarian tissue cryopreservation can be applied to prepuberal patients because techniques requiring ovarian stimulation are not suitable because of the absence of maturation of the hypothalamic-hypophyseal-ovarian axis. That is why it is impossible to apply efficient techniques of oocyte Histological biopsy of a prepuber ovarian Histological biopsy of an adult ovarian cryopreservation or embryo cryopreservation in adult woman. The main fact is We can see primordial follicles in the cortical region. We can see primary follicles, antral follicles and Graaf follicles that they require the production of mature oocytes. The Ovarian Tissue Cryopreservation is the only fertility preservation technique in prepuberal patients. Ovarian tissue cryopreservation Cortical tissue Orthotropic transplant Natural conception Propitious environment for follicular development Whole ovary Heterotopic transplant Limited for the Difficult neovascularization Follicular number of grafts which committed graft viability development used in the Less propitious environment transplant because monitoring for follicular development of the ovarian size Easy and monitoring follicular FIV and ICSI are necessary for Invasive recuperation conception surgery Transplant with pedicle Absence of gonadotropin response for follicular maturation POI 9p13 CHILDHOOD CANCER Chemotherapy Radiotherapy Irreversible gonadal damage, especially in the granulose cells, which can not produce estrogens Depending on the age of exposition, the duration, and the zone to be radiated Long duration surgery Fast introduction and extraction of cryoprotector inside all cells of the ovary CLASSIC GALACTOSEMIA (1:16.000/60.000) Deleterious mutations in GALT His not a well-established protocol yet Immediate administration of blood to the graft during the transplant POI Possible ischemia due to thromboembolism in vascular pedicle More probability of the reintroduction or cancer cells due to the use of medulla ovarian tissue Reduction in the patient’s follicles number, making spontaneous conception less probable Possibility of reintroduction of cell cancer in the transplant. It is necessary to develop cell tumor detection techniques in the ovarian tissue before the transplant. But only in cancer types with high probability of metastasis in the ovary CONCLUSIONS In childhood patients the current technique is ovarian tissue cryopreservation due to the other techniques used in adults with better results, like oocyte and embryo cryopreservation, can not be used in this patients. Other new techniques, like ovary transposition, in vitro oocyte maturation, follicular cultures or co – treatment with GnRH analogs, will be good options in a prepuberal female patient that wants to preserve her fertility, but these are still in developmental phases and present high risk for the patients. In galactosemia cases we have to consider the possibility of primary insufficiency ovarian reversion and spontaneous conception, whereas, in childhood cancer cases we have to consider the possibility of the reintroduction of cancer cells within the transplant. For this reason, it is recommended to perform cancer cell detection techniques in cancer types which have high risk of causing ovarian metastasis. Oocyte and embryo donations and adoption are options that should be considered. BIBLIOGRAPHY Ovarian tissue cryopreservation: a committee opinion. The Practice Commitee of American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertility and Sterility 2014:101(5); 1237-43. Britt van Erven, Cynthia S Gubbels, Ron J van Golde et al. Fertility preservation in female classic galactosemia patients. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2013, 8:107 Murat Sonmezer, Kutluk Okatay. Fertility preservation in female patients. Human Reproduction Update, Vol.10, No.3 pp.251-266,2004