New chemotherapy drugs in metastatic breast cancer Guy Jerusalem, MD, PhD

New chemotherapy drugs in
metastatic breast cancer
New chemotherapy drugs in
metastatic breast cancer
Guy Jerusalem, MD, PhD

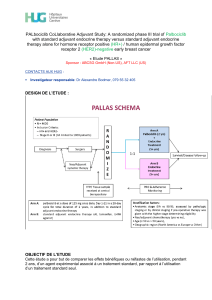
MBC Patients’ survival over time
MBC Patients’ survival over time
Median survival increases over time, but is still measured in months
This is not yet a chronic disease
Median survival increases over time, but is still measured in months
This is not yet a chronic disease

New chemotherapy drugs in
metastatic breast cancer
New chemotherapy drugs in
metastatic breast cancer
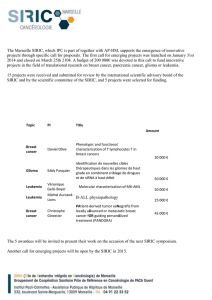
•Erubiline
•Nab-paclitaxel
•Etirinotecan pegol (NKTR-102)

Eribulin Inhibits Microtubule Dynamics
in the Mitotic Spindle
Eribulin Inhibits Microtubule Dynamics
in the Mitotic Spindle
Growing
microtubule
Shortening
microtubule
Tubulin
Polymerization
Tubulin
Depolymerization
Spindle
Pole
Eribulin
1. Inhibits microtubule growth
Nonproductive
tubulin aggregates
Eribulin
3. Generation of nonproductive
tubulin aggregates
2. No measurable effect on
shortening (at relevant
concentrations)
Adapted from Jordan MA et al. Mol Cancer Ther 2005; 4:1086-1095.

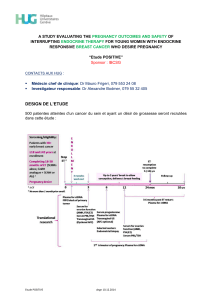
Eribulin Blocks Microtubule Growth by
Binding to Microtubule Ends
Eribulin Blocks Microtubule Growth by
Binding to Microtubule Ends
(-) end
(+) end
(+) end
(-) end
β
Eribulin binds to (+)
ends Vinblastine binds to (+)
ends and along sides Paclitaxel binds to inside
surface
Paclitaxel
α
αα
α
Eribulin Vinblastine
(+) end
(-) end
β
α
αα
α
Modified from Jordan MA and Wilson L, Nat RevCancer. 2004;4:253-65, and Smith JA, Biochemistry, 2010:49, 1331-1337
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
1
/
44
100%