PRESENTER DES FAITS DIVERS A LA MANIERE D`UN

PRESENTER DES FAITS DIVERS A LA MANIERE D’UN JOURNALISTE
Utiliser le discours indirect
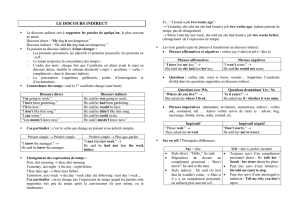
Lorsqu’on parle au discours direct, on rapporte les paroles précises d’une personne en citant ce qu’elle a dit
entre guillemets.
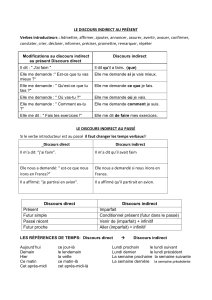
Lorsqu’on parle au discours indirect, et c’est très souvent le cas lors de reportages radio ou télévisés, on
explique ce qui a été dit en utilisant des verbes de parole comme say ou tell, et une proposition qui
commence par that.
FORM = subject + reporting verb + that + what has been said
sujet + verbe de parole + that + paroles
Attention !!
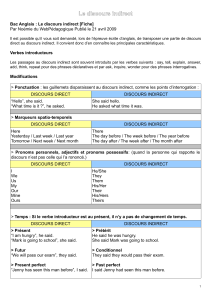
Quelques changements sont nécessaires lorsqu’on parle au discours indirect.
Pronouns
Time and place expressions
Modals
I he / she
you he / she
we they
me him / her
my his / her
our their
now then
today that day
this that
here there
will would
can could
may might
Examples:
The teacher said that she was afraid during the school shooting.
The gunman told the police that he wanted revenge.
Discours direct: The parents said: “We are worried that a mass shooting can happen again.”
Discours indirect: The parents said that they were worried that a mass shooting could happen again.

PRESENTER DES FAITS DIVERS A LA MANIERE D’UN JOURNALISTE
Utiliser le discours indirect
Lorsqu’on parle au discours direct, on rapporte les paroles précises d’une personne en citant ce qu’elle a dit
entre guillemets.
Lorsqu’on parle au discours indirect, et c’est très souvent le cas lors de reportages radio ou télévisés, on
explique ce qui a été dit en utilisant des verbes de parole comme say ou tell, et une proposition qui
commence par that.
FORM = subject + reporting verb + that + what has been said
sujet + verbe de parole + that + paroles
Attention !!
Quelques changements sont nécessaires lorsqu’on parle au discours indirect.
Pronouns
Time and place expressions
Modals
I he / she
you he / she
we they
me him / her
my his / her
our their
now then
today that day
this that
here there
will would
can could
may might
Examples:
The teacher said that she was afraid during the school shooting.
The gunman told the police that he wanted revenge.
Discours direct: The parents said: “We are worried that a mass shooting can happen again.”
Discours indirect: The parents said that they were worried that a mass shooting could happen again.
1
/
2
100%